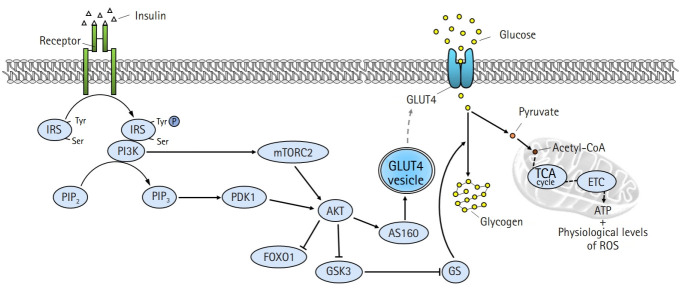
Fig. 2.
Intracellular insulin signaling pathway in skeletal muscle. Binding of insulin to insulin receptors (IR) on the plasma membrane promotes tyrosine autophosphorylation at the IR, which in turn induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the IR substrate (IRS). IRS activates the downstream substrate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway, and the activated AKT leads to increased glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis by inducing phosphorylation of AKT substrate of 160 kDa (AS160) and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), respectively. Activated AS160 increases glucose uptake by mediating the translocation of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. Intracellular glucose is used for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation and glycogen synthesis. Tyr, tyrosine; Ser, serine; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate; PDK1, phosphatidylinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; mTORC2, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2; FOXO1, forkhead box protein O1; GS, glycogen synthase; acetyl-CoA, acetyl coenzyme A; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; ETC, electron transport chain; ROS, reactive oxygen species.