FIGURE 1.
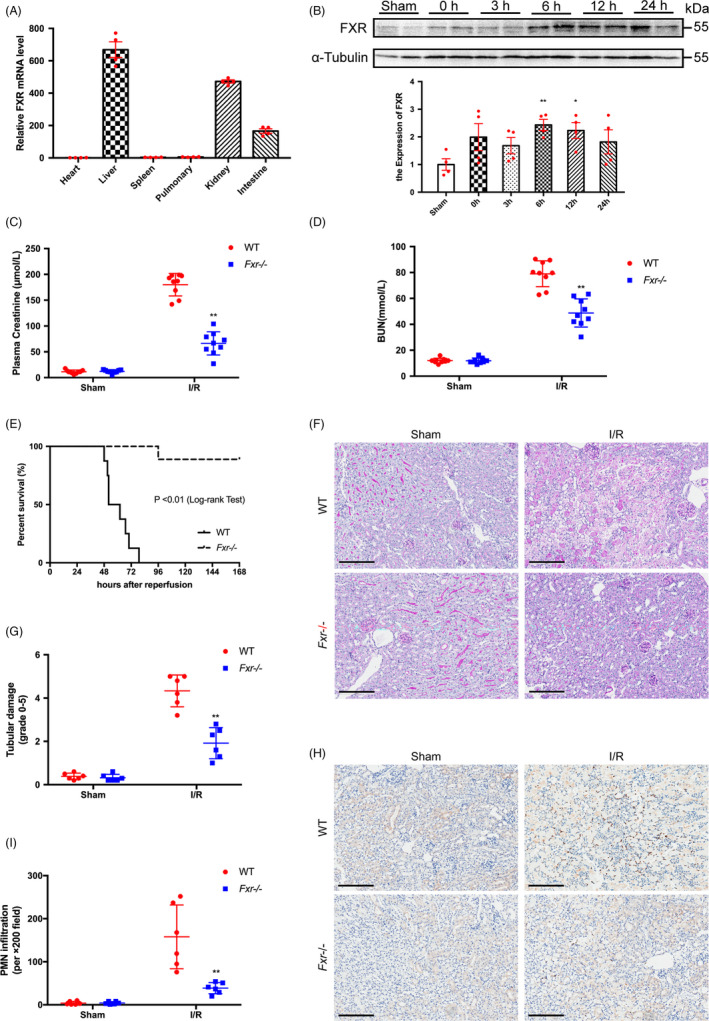
FXR deficiency alleviates kidney injury after I/R. (A) FXR is expressed in the kidney. Total RNA was extracted from the indicated tissues of wild‐type mice, and FXR mRNA levels were measured by RT‐PCR. Results are plotted as the fold change relative to mRNA levels in heart (n = 4). (B) Time courses of FXR protein expression in the kidney after I/R were measured by WB. Whole cell lysates of the kidney tissues at 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h and 24 h after reperfusion were analysed (n = 4). Plasma creatinine (C) and BUN (D) concentrations were measured at 24 h after the initiation of reperfusion in wild‐type (WT) and Fxr−/− mice (n = 9 per group). (E) Kaplan‐Meier Estimates of survival among wild‐type and Fxr−/− mice (n = 20 per group) after renal I/R injury (log‐rank test, P < 0.01). (F) PAS staining and (G) quantitative data of the tubular injury score of post‐I/R kidneys harvested at 24 h (original magnification, ×200; scale bar, 200 μm) (n = 6 per group). (H) Representative renal myeloperoxidase (MPO) staining (original magnification, ×200; scale bar, 200 μm) (n = 6 per group). (I) The number of infiltrating MPO‐positive cells in the post‐I/R kidney. Each column represents the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs sham (B) or wild‐type mice at the same time point after I/R injury (C‐I)
