Extended Data Fig. 7. Retrograde CTB labeling of motor pools enables the identification of transcriptionally distinct classes of fast and slow-firing motor neurons in the adult spinal cord.
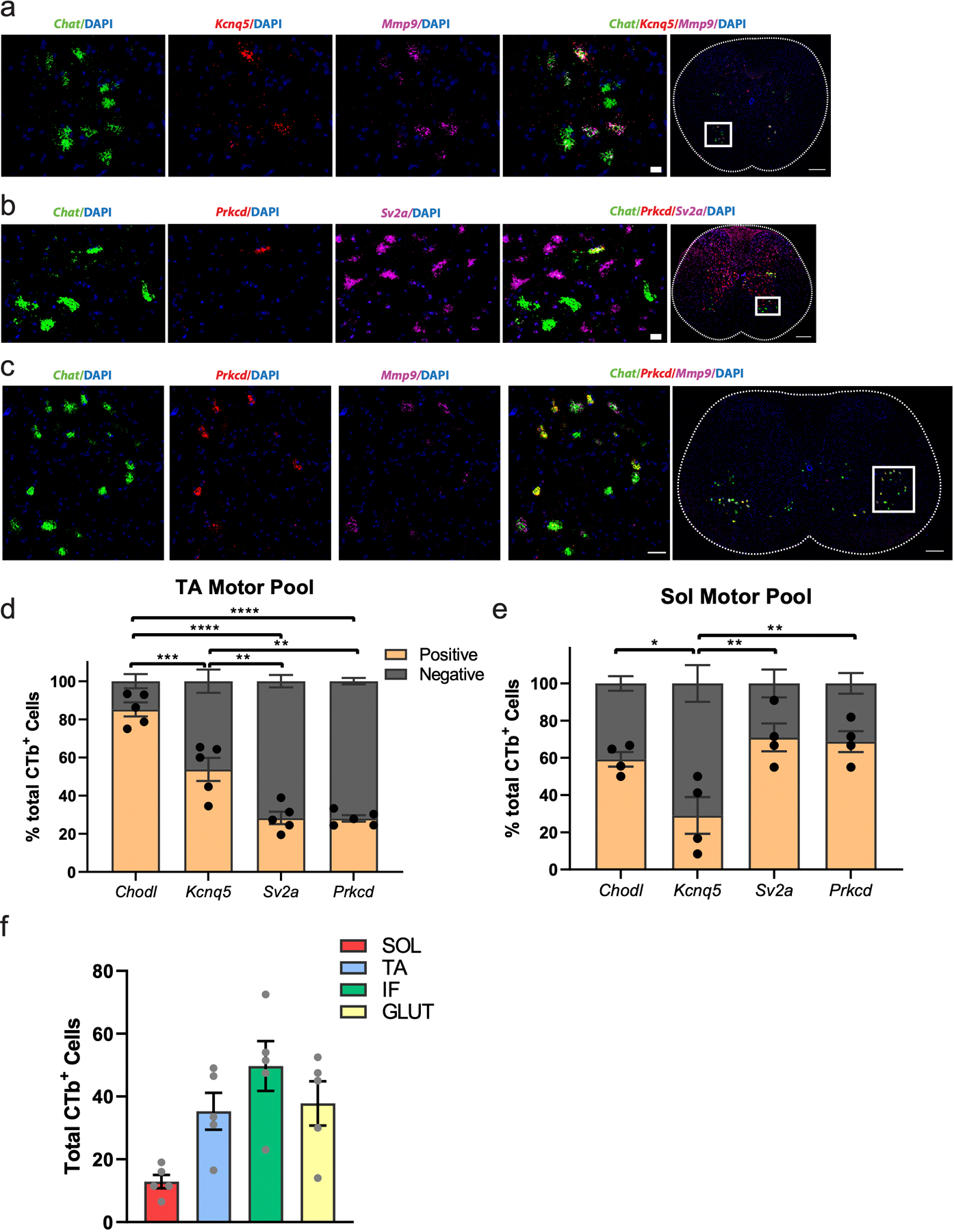
a, Representative in situ hybridization against Chat/Mmp9/Kcnq5 in transverse spinal cord shows that Kcnq5 is expressed in a subset of Mmp9+ fast-firing motor neurons. n=4 biologically independent animals. Scale bar=20 µm inset and 200 µm overview. b, Representative in situ hybridization against Chat/Sv2a/Prkcd in transverse spinal cord shows that Prkcd is expressed in almost every Chat+/Sv2a+ slow-firing motor neuron. n=2 biologically independent animals. Scale bar=20 µm inset and 200 µm overview. c, Representative in situ hybridization against Chat/Mmp9/Prkcd in transverse spinal cord shows that Prkcd is excluded from almost every Chat+/Mmp9+ fast-firing motor neuron. n=4 biologically independent animals. Scale bar=30 µm inset and 200 µm overview. d-e, Proportion of cells expressing fast and slow-firing markers in the CTB-labeled TA (d) and SOL (e) motor pools. There is a significantly higher proportion of cells expressing both known and novel fast-firing markers in TA than SOL (d), and a higher proportion of cells expressing both known and novel slow-firing markers in SOL than TA. Adjusted p-value=0.0456 (Chodl+>Kcnq5+). f, Total number of CTB-positive cells labeled across biologically independent animals. One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey multiple comparison test among all conditions. n=4–5 biologically independent animals (d-f). *=p value<0.05, **=p value <0.01, ***=p value<0.001, ****=p value<0.0001. Error bars are SEM.
