Extended Data Fig. 4. Vipr2 and Npas1 are novel, robust, and specific markers of α and γ motor neurons in the spinal cord.
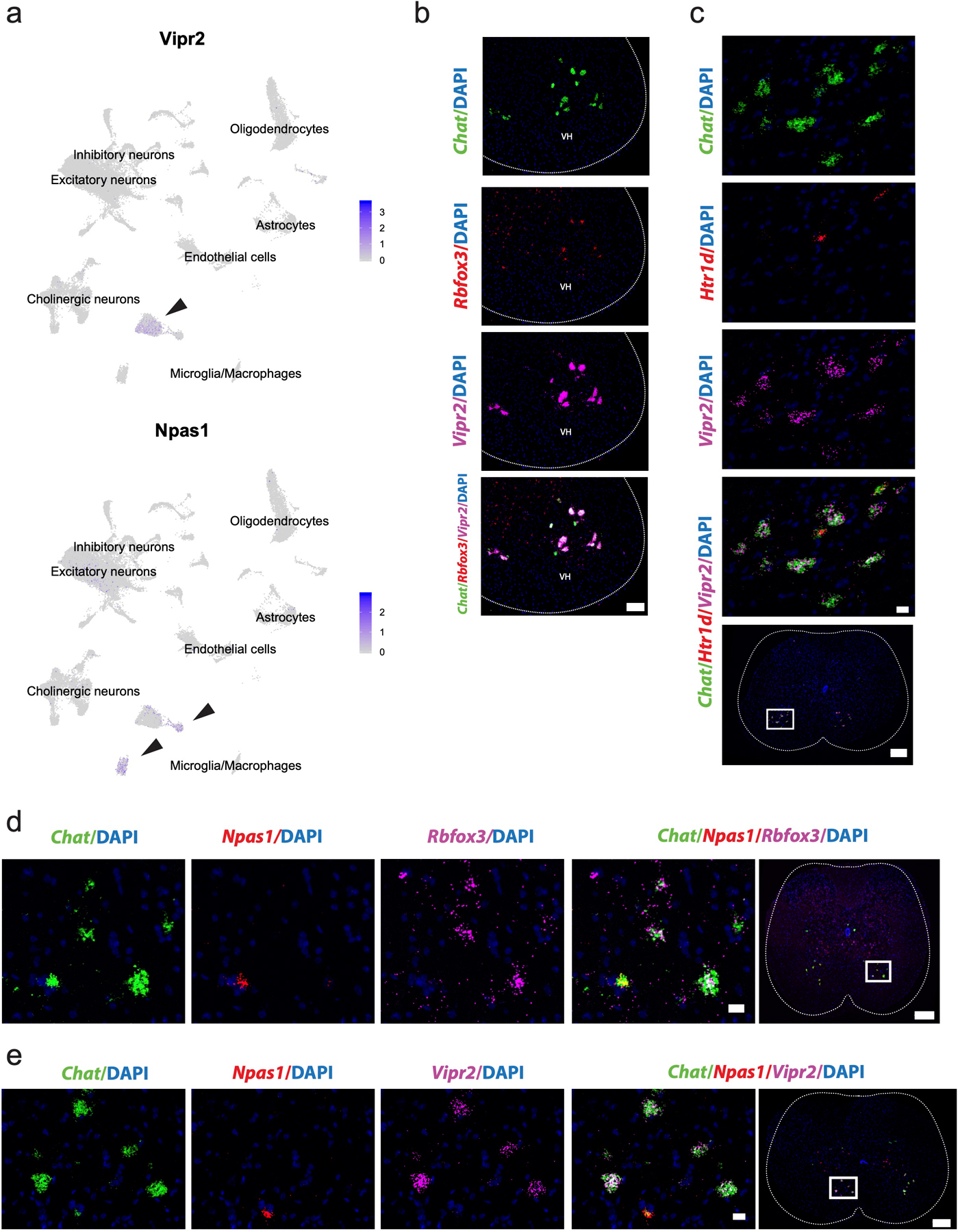
a, Average expression of Vipr2 and Npas1 across all spinal cord cell populations (labeled), overlaid on UMAP. Arrow points to α and γ motor neuron clusters, respectively. b, Representative in situ hybridization against Chat/Rbfox3/Vipr2 in transverse spinal cord shows coexpression in the ventral horn (VH). n=4 biologically independent animals. Scale bar=100 µm. c, Representative in situ hybridization against Chat/Htr1d/Vipr2 in transverse spinal cord shows mutual exclusion. Scale bar=50 µm (inset) and 200 µm (overview). n=4 biologically independent animals. d, Representative in situ hybridization against Chat/Npas1/Rbfox3 in transverse spinal cord shows mutual exclusion of Rbfox3 and Npas1 in Chat+ cells. n=5 biologically independent animals. Scale bar=20 µm (inset) and 200 µm (overview). e, Representative in situ hybridization against Chat/Npas1/Vipr2 in transverse spinal cord shows mutual exclusion of novel markers Vipr2 and Npas1 in Chat+ cells. n=4 biologically independent animals. Scale bar=20 µm (inset) and 200 µm (overview).
