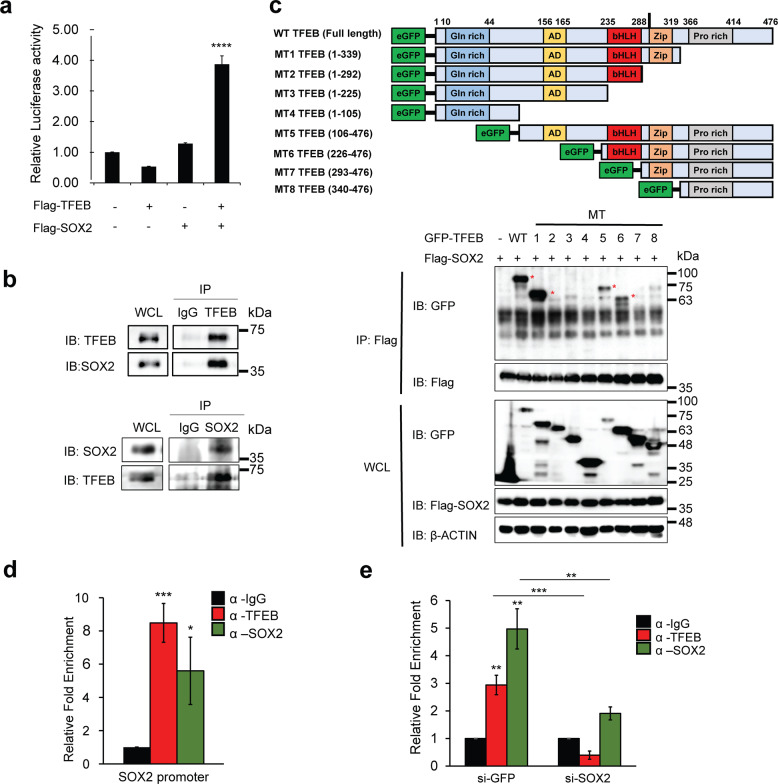
Fig. 3. TFEB interacts with Sox2 to enhance the expression of Sox2.
a Co-expression of TFEB and Sox2 significantly enhanced the Sox2 promoter-driven luciferase activity in HEK293T cells. b TFEB interacts with Sox2 at the endogenous level. Immunoprecipitates using mESC lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated antibodies. c HEK293T cells were co-transfected with Flag-Sox2, wildtype (WT) TFEB, and various truncated mutant forms of TFEB (MT1-MT8) as indicated in the figure. Abbreviations of each domain are as followed: glutamine-rich (Gln rich), activation domain (AD), basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH), leucine zipper (Zip), and proline-rich (Pro rich). Asterisks (*) indicate interaction. bHLH and Zip domains of TFEB interact with Sox2. d ChIP-qPCR analysis was performed by pulling-down with anti-TFEB antibody and anti-Sox2 antibody, following which qPCR targeting the Sox2 binding site at the genomic DNA level in mESCs was performed. e Sox2 was knockdown before harvested for ChIP-qPCR analysis. Anti-TFEB antibody and anti-Sox2 antibody were used for pull-down, following which qPCR targeting the Sox2-binding site at the genomic DNA level in mESCs was performed. All statistical analyses represent average values of a representative experiment from at least two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD values of triplicate assays. Data are shown as mean ± SD, n = 3. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 ****p < 0.0001 compared to the corresponding control group. The student’s t test was used for all statistical analysis.