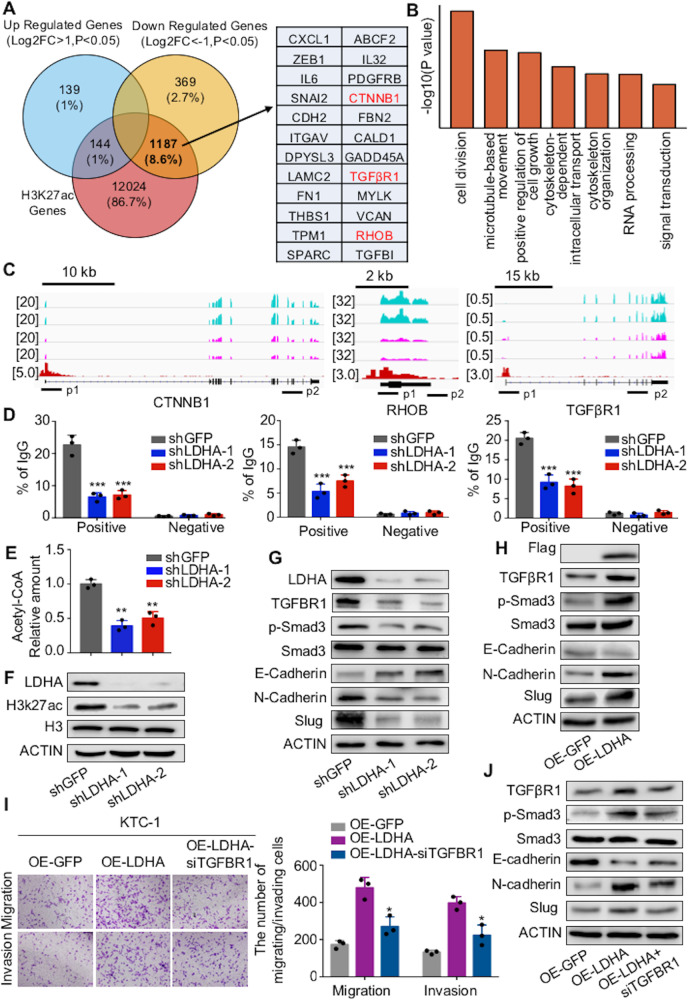
Fig. 6. LDHA promotes the transcription of genes involved in the EMT process.
A Venn diagram illustrating the overlap between genes from the RNA-Seq data after LDHA knockdown and genes from the ChIP-Seq data of H3K27ac modification in B-CPAP cells. B Summary of the significantly enriched pathways of the downregulated genes bound by H3K27ac. C RNA-Seq peaks of CTNNB1, RHOB, and TGFβR1 treated with LDHA knockdown, as well as H3K27ac binding peaks, are shown. D ChIP-qPCR was performed with B-CPAP cells using H3K27ac and IgG antibodies to determine the expression levels of CTNNB1, RHOB, and TGFβR1. E Intracellular acetyl-CoA levels were measured in B-CPAP cells treated with LDHA knockdown. F H3K27ac levels were decreased after LDHA knockdown in B-CPAP cells. G, H Western blot assays showed the changes in TGFβR1, phosphorylated Smad3, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and Slug in B-CPAP cells with LDHA knockdown and in KTC-1 cells expressing LDHA. I Transwell assays indicated that the knockdown of TGFβR1 partially reversed the increased migration and invasion ability of KTC-1 cells expressing LDHA. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. J KTC-1 cells stably expressing LDHA were infected with siRNA targeting TGFβR1. Western blotting was used to detect the expression levels of TGFβR1 and the phosphorylation levels of Smad3, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and Slug. All *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.