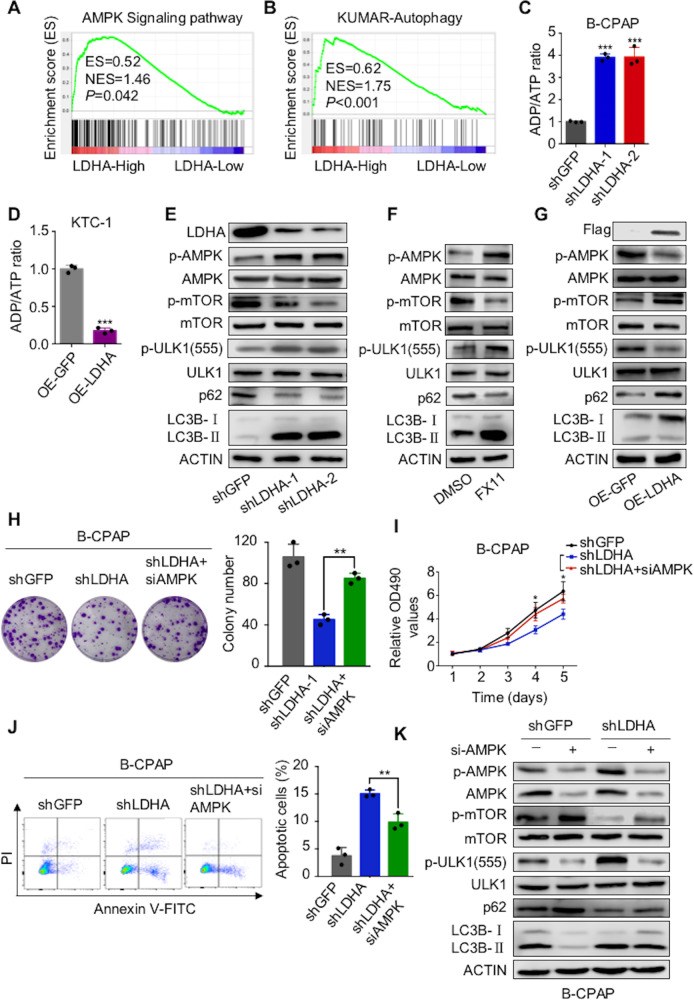
Fig. 7. LDHA regulates tumorigenesis and autophagy through the AMPK signaling pathway.
A, B Gene expression data acquired from the TCGA database were subjected to GSEA v2.2.0; the results showed that LDHA expression was correlated with AMPK signaling and autophagy-related pathways. C, D The ADP/ATP ratio assay showed that LDHA knockdown increased the ADP/ATP ratio in B-CPAP cells, whereas overexpression of LDHA decreased the ADP/ATP ratio in KTC-1 cells. E–G Western blotting was used to detect phosphorylated AMPK, phosphorylated mTOR, phosphorylated ULK1, p62, and LC3BII/I in B-CPAP cells treated with LDHA knockdown or FX11 (10 μM for 24 h) and in KTC-1 cells treated with LDHA expressing. Colony formation assay H and CCK-8 assay I showed that AMPK knockdown partially attenuated the inhibited proliferation induced by LDHA knockdown in B-CPAP cells. J Flow cytometry indicated that AMPK knockdown partially reversed the apoptosis induced by LDHA knockdown in B-CPAP cells. K B-CPAP cells stably knocking down LDHA were infected with siRNAs targeting AMPK. Western blotting was used to detect phosphorylated AMPK, phosphorylated mTOR, phosphorylated ULK1, p62, and LC3BII/I expression levels. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. All *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.