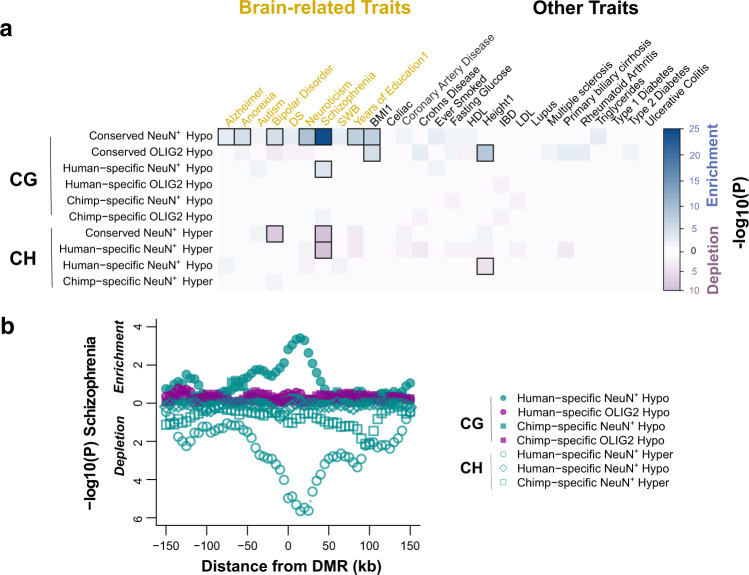
Fig. 4. Evolutionary DMRs contribute to brain disease susceptibility.
a Significance levels for the enrichment for genetic heritability in different DMRs (+/-25kb) and complex traits. Both conserved and human-specific neuronal DMRs are associated with schizophrenia. Enrichment with FDR < 0.05 are highlighted in squares. Notably, CG DMRs hypomethylated in NeuN+ cells compared to OLIG2+ cells in all three species (conserved NeuN+ hypo) are highly enriched in variants for several brain-related traits, and human-specific NeuN+ hypo shows enrichment in schizophrenia. b A sliding-window analysis further demonstrates that the aforementioned signal for schizophrenia was centered at the DMRs and did not originate from extended adjacent regions. The y-axis represents the P-values in sliding windows around DMRs classified by species (human or chimpanzee), cell-type (NeuN+ or OLIG2+), and cytosine context (mCG or mCH). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.