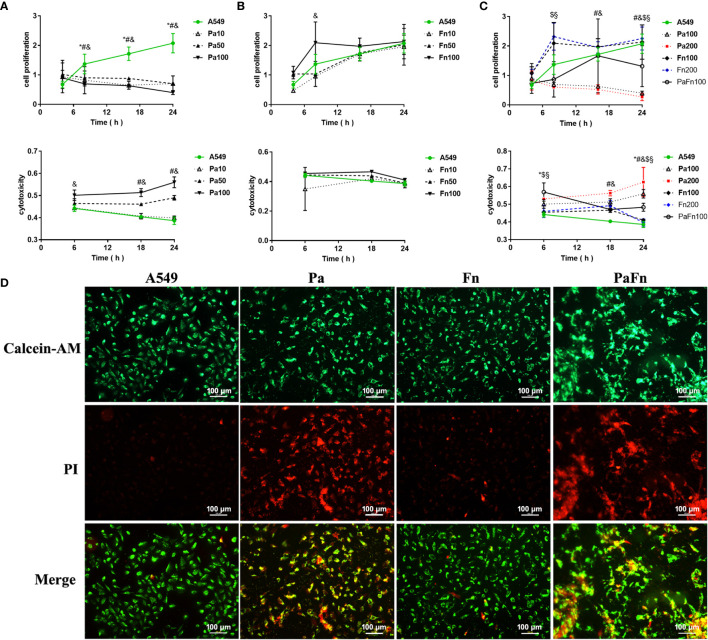
Figure 3.
The effect of P. aeruginosa and F. nucleatum on cellular proliferation and cytotoxicity. (A) The effect of P. aeruginosa on cell proliferation and cytotoxicity of pulmonary epithelial cells. A549 cells were infected with different MOI (10, 50, 100) of P. aeruginosa. * Pa10 compared with A549, # Pa50 compared with A549, & Pa100 compared with A549. (B) The effect of F. nucleatum on cell proliferation and cytotoxicity of pulmonary epithelial cells. A549 cells were infected with different MOI (10, 50, 100) of F. nucleatum. * Fn10 compared with A549, # Fn50 compared with A549, & Fn100 compared with A549. (C) The effect of the simultaneous infection of P. aeruginosa and F. nucleatum on cell proliferation and cytotoxicity of pulmonary epithelial cells. A549 cells were simultaneously infected with P. aeruginosa (MOI 100) and F. nucleatum (MOI 100), and the single P. aeruginosa or F. nucleatum infection groups (MOI 100, 200) were used as control. * A549 compared with PaFn100, # Pa100 compared with PaFn100, & Pa200 compared with PaFn100, $ Fn100 compared with PaFn100, § Fn200 compared with PaFn100. */#/&/$/§ P<0.05, statistics were achieved by analysis of variance followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Representative fluorescence images of pulmonary epithelial cells infected with P. aeruginosa and F. nucleatum alone or together. A549 cells were infected with P. aeruginosa (MOI 100) and F. nucleatum (MOI 100) alone or together for 24 h. Pa, P. aeruginosa; Fn, F. nucleatum.