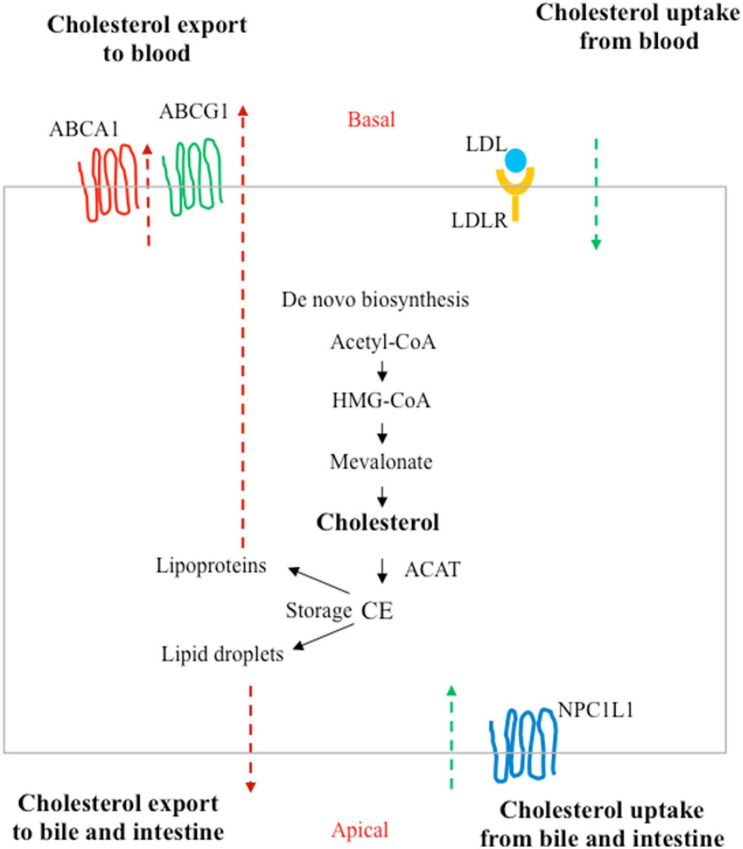
FIGURE 3.
Homeostasis of cholesterol in a polarized cell. In addition to de novo biosynthesis, cholesterol carried by low-density lipoprotein (LDLs) in the blood can be taken up by LDL receptors (LDLRs) at the basal surface of the polarized cells (such as enterocytes or hepatocytes). Niemann–Pick type C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) can absorb free cholesterol from dietary sources by enterocytes in the intestine and from bile in the biliary ducts by hepatocytes in the liver. Excess cholesterol is exported to the blood by ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1) or the subfamily G member 1 (ABCG1). Cholesterol can also be converted to cholesteryl ester (CE) by acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) for storage in lipid droplets or for secretion as lipoproteins.