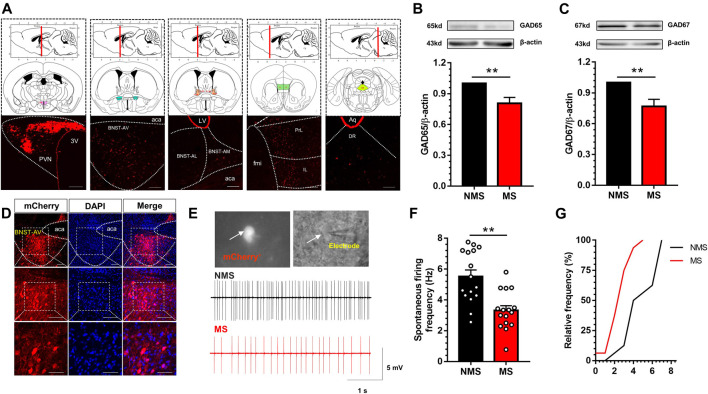
FIGURE 3.
Excitation of GABA neurons in BNST-AV region was decreased in mice with MS-induced chronic visceral pain (A) Luma was absorbed by PVN neurons and directly transmitted to mPFC, BNST-AV, BNST-AL, BNST-AM and DR (3V, third ventricle; fmi, forceps minor of corpus callosum; PrL: prelimbic cortex; IL: infralimbic cortex; aca, anterior limb of ac; LV, lateral ventricle; Aq, mesencephalic aqueduct; DR: dorsal raphe nucleus). scale bar = 100μm (B–C) Western blot analysis of GAD65 and GAD67 protein in the BNST-AV demonstrated that MS mice presented significant decrease in the expression of GAD65 protein (B, n = 6; **p < 0.01) and GAD67 (D, n = 6; **p < 0.01) compared with NMS group (D) The localization of GABAergic BNSTAV-PVN neurons via PVN-injected retrograde rAAV-Ef1α-DIO-mCherry-WPRE-pA in Vgat-Cre mice. Scale bar = 100μm except for the bottom marked by 50μm (E) The schema of spontaneous firing frequency in GABAergic neurons in BNST-AV regions (F) The spontaneous firing frequency of GABA neurons (mCherry+) in MS group was significantly decreased vs. NMS group (n = 16, six mice per group; **p < 0.01) (G) The cumulative frequency distribution curves in MS groups were evidently shifted leftward.