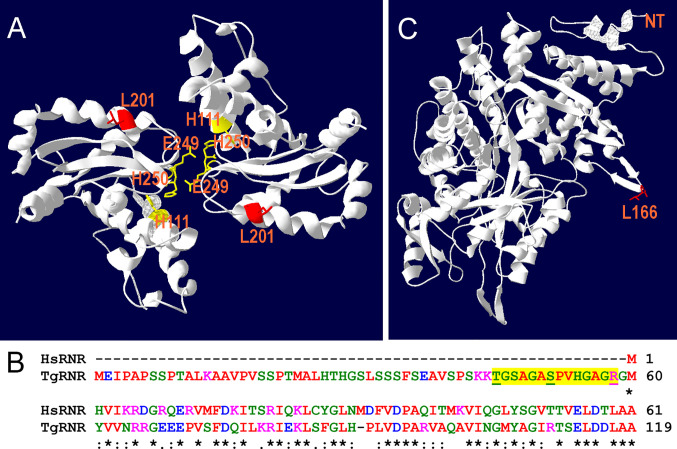
Figure 4.
Location of substitutions in TgSOD2 and TgRNR. (A) SOD forms dimers that coordinately bind to iron cofactors at their interface. The Toxoplasma amino acid sequence was threaded onto a Plasmodium knowlesi protein structure (PDB 2AWP) to create a model for TgSOD2. The mutation at position 201 (red) is near to the end of an α-helix; substitution of a proline for leucine at this location likely causes the helix to bend. This mutation is also proximal to key iron-coordinating residues H111, E249 and H160. (B) Alignment of the Toxoplasma and human RNR sequences indicates that TgRNR has a novel 59 amino acid N-terminal extension. MS peptides (yellow highlight) in ToxoDB map to this sequence with S and T phosphorylated, and R monomethylated (underlined). (C) The Toxoplasma amino acid sequence for RNR was threaded onto the human RNR structure (PDB 3HND) to create a model for TgRNR. The L166Q mutation is in a solvent exposed loop, that is poorly conserved and not known to contribute to enzyme interactions.