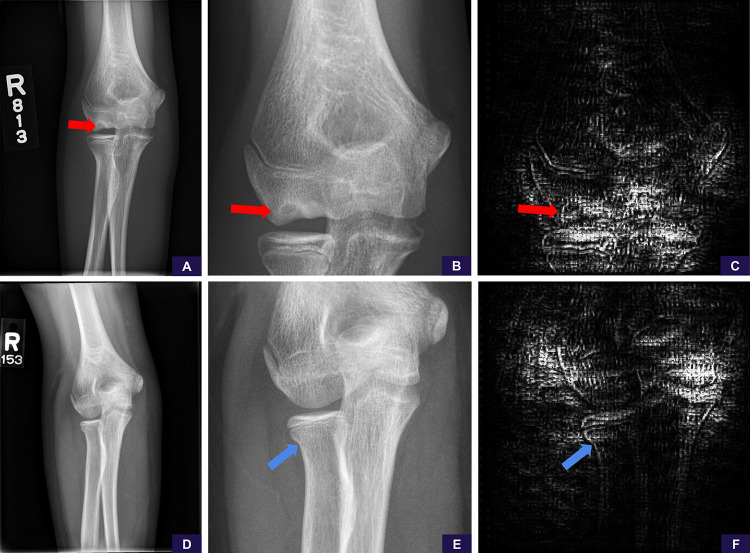
Figure 6:
False-negative examples of, A–C, rare abnormality (osteochondral lesion) and, D–F, subtle abnormality (nondisplaced radial neck fracture). A, Source anteroposterior view is sufficient to identify the osteochondral lesion (red arrow). B, Image cropped and magnified to the area of interest shows the abnormality more clearly. Reinterpretation with the magnified image has no meaningful change in positivity score from 0.25 (negative, high confidence) to 0.24 (negative, high confidence). C, Saliency map demonstrates the model is not attentive to the abnormality and is examining the cortices around the joint, ultimately concluding (falsely) that this is a negative study for abnormality. D, Source anteroposterior view shows resolution detail is insufficient to identify the radial neck fracture. E, Image cropped and magnified to the area of interest shows the radial neck fracture (blue arrow). Reinterpretation with the magnified image has no meaningful change in positivity score from 0.19 (negative, high confidence) to 0.21 (negative, high confidence). F, Saliency map demonstrates the model is not sufficiently attentive to the abnormality, focusing elsewhere and ultimately concluding (falsely) this is a negative study for abnormality.