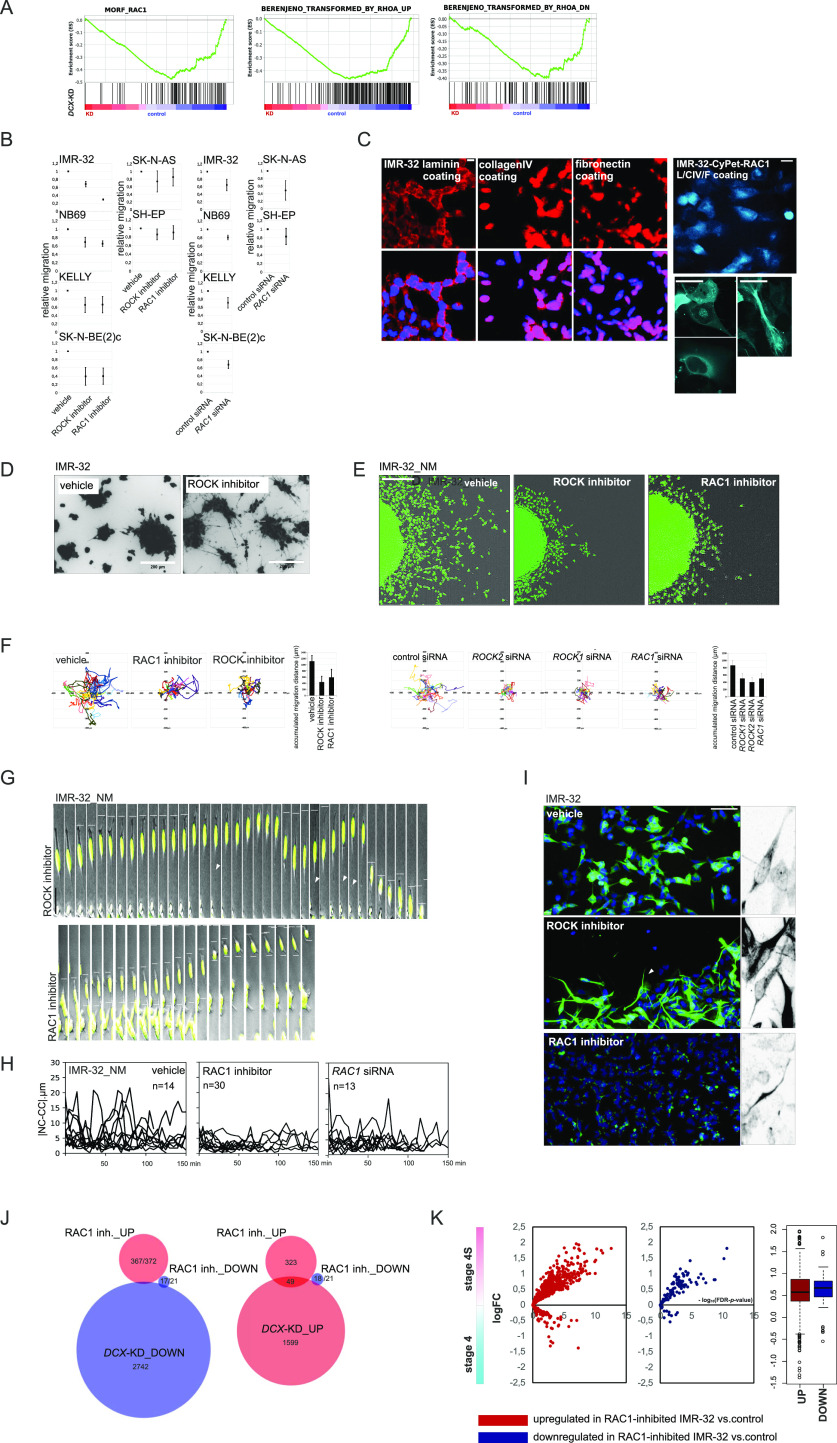
Figure 4. ROCK and RAC1 inhibition interferes with cell detachment and NUC.
(A) Gene set enrichment analysis plots showing RHOA-related and RAC1-related gene sets in DCX-KD IMR-32 versus control. (B) 2D exclusion assay in NB cell lines after treatment with the RAC1 inhibitor or ROCK inhibitor and after RAC1 RNAi (left). Relative cell migration (right) is quantified by normalization of cell density to vehicle- or control siRNA-treated cells. Mean relative difference values ± SD are presented. (C) RAC1 immunostaining and CyPet-RAC1 subcellular localisation in IMR-32 (L, laminin; CIV, collagen IV; F, fibronectin). Scale bar 20 μm. (D) Images of IMR-32 spheroids stained with Calcein AM after 72 h of treatment with vehicle or ROCK inhibitor in pseudo 3-D. (E) Random walk plots in IMR-32_NM treated with vehicle, RAC1 inhibitor or ROCK inhibitor for 72 h (13 h, 15-min intervals). Scale bar 200 μm. (F) Accumulated migration distances of control, ROCK inhibitor– and RAC1 inhibitor–treated IMR-32_NM cells and after ROCK1, ROCK2, or RAC1 RNAi. Mean migration distances + SD are presented. (G) Time-lapse images of IMR-32_NM after treatment with ROCK inhibitor (left) or RAC1 inhibitor (right). Nuclei and cell leading edges of migrating cells are indicated. Scale bar 20 μm. (H) |NC-CC| plots in control IMR-32_NM and after treatment with the RAC1 inhibitor or RNAi against RAC1. (I) βIII-tubulin immunolabeling in IMR-32 after treatment with vehicle, ROCK- or RAC1 inhibitor. Fork-like structures are showed in grayscale negative field. Scale bar 100 μm. (J) Venn diagrams showing the numbers of genes in DCX-KD ∩ RAC1 inhibitor transcriptomic overlap (P-values ≤ 0.09; |logFC| cutoff [DCX-KD]: 0.3, |logFC| cutoff [RAC1 inhibitor]: 0.2). (K) Volcano plots showing expression of DEGs in RAC1-inhibitor-treated IMR-32 in stage 4S versus 4 tumors.