Figure 1.
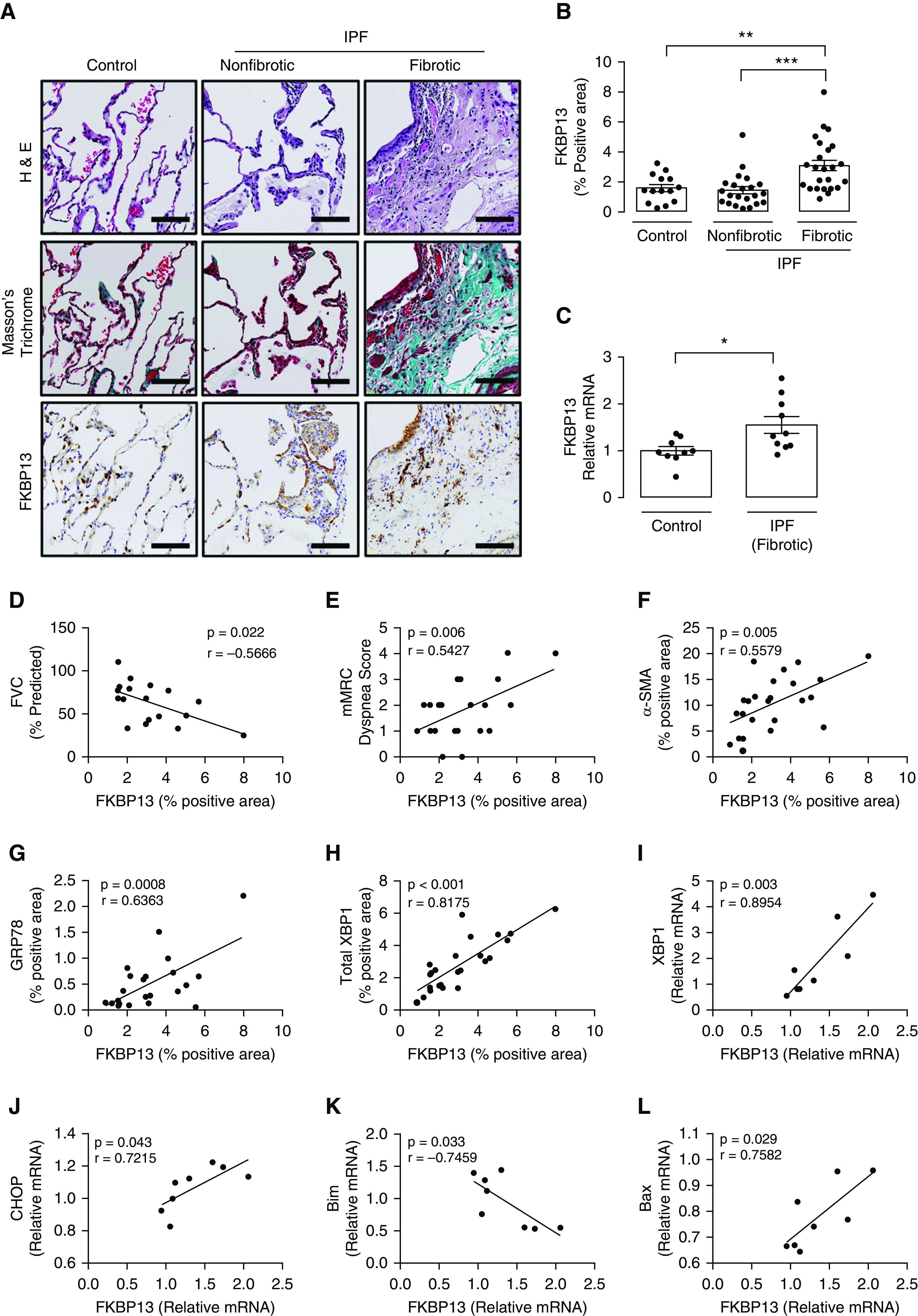
FKBP13 (13-kD FK506-binding protein) expression is elevated in fibrotic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) tissue and is correlated with disease severity, ER stress, and apoptosis markers. A tissue microarray containing fibrotic and nonfibrotic cores from 24 patients with IPF and 17 control subjects was stained for FKBP13 and other markers by using immunohistochemistry (IHC) and was quantified by using HALO image-analysis software. The NanoString nCounter platform was used to assess the gene expression of unfolded protein response (UPR) and apoptosis markers in the extracted cores. (A and B) Representative FKBP13 immunostaining images and quantification by HALO. Corresponding Masson’s Trichrome and H&E staining from serial sections are shown. Images were acquired using the automated Olympus VS120 slide scanner, which utilizes a stitching algorithm to reconstruct the whole specimen from overlapping image tiles. (C) Comparison of FKBP13 mRNA expression in fibrotic IPF and control tissue cores by NanoString gene expression analysis. (D–H) Correlation of FKBP13-positive immunostained area with percent-predicted FVC; mMRC dyspnea score; and α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin)-, GRP78 (glucose-regulated protein 78)-, and total XBP1–positive area. (I–L) Correlation of FKBP13 mRNA expression with XBP1, CHOP (C/EBP-homologous protein), Bim, and Bax in the fibrotic regions of human IPF lung tissues. Each point represents the average protein or mRNA expression value for an individual patient. Data is presented as mean ± SEM. Scale bars, 100 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus control. ER = endoplasmic reticulum; FVC = forced vital capacity; H&E = hematoxylin and eosin; mMRC = modified Medical Research Council.
