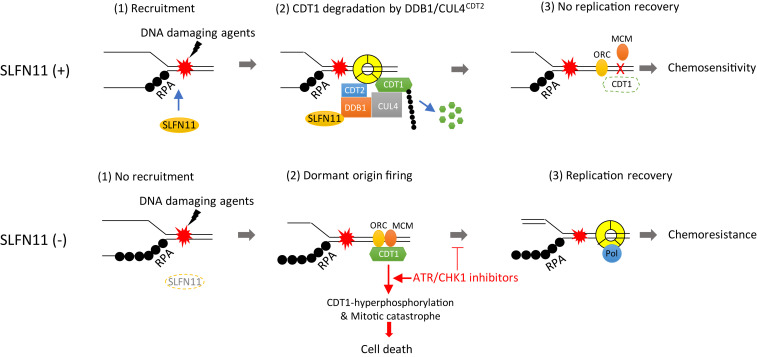
Fig. 6.
Proposed model for SLFN11-mediated replication reactivation block and synthetic lethality of ATR/CHK1 inhibitors in SLFN11-negative cancer cells. In SLFN11-proficient cells, SLFN11 is recruited to chromatin by DNA damage. It subsequently binds to DDB1 and promotes the degradation of CDT1 and other substrates as a cofactor of activated DDB1–CUL4CDT2. Consequently, CDT1-mediated replication recovery is irreversibly blocked, leading to sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. In SLFN11-deficient cells, conversely, DDB1–CUL4CDT2-mediated degradation of CDT1 is reduced. CDT1 then promotes replication recovery by activating dormant origins, resulting in chemoresistance. Treatment of ATR/CHK1 inhibitor reverses chemoresistance of SLFN11-deficient cells by inducing premature replication and mitosis through CDT1 phosphorylation, which induces mitotic catastrophe and cell death.