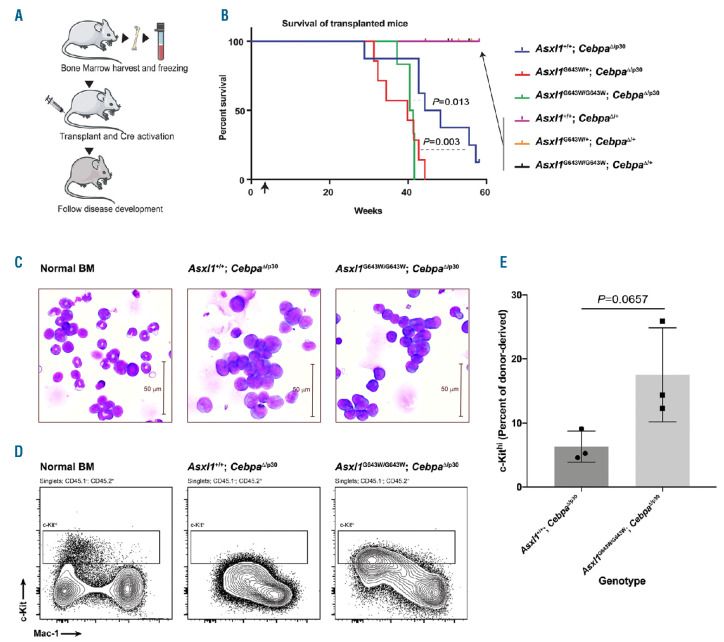
Figure 3.
The ASXL1G643W variant accelerate CEBPA mutant acute myeloid leukemia. (A) Schematic outline of the experiment. Briefly, bone marrow (BM) was harvested from mice with different genotypes and then transplanted into cohorts of irradiated recipients. Three weeks after the transplant, mice were injected with pIpC and subsequently observed for signs of disease development over a period of 60 weeks. (B) Kaplan-Meyer survival curve of transplanted mice. The arrow indicates the time point for injection with pIpC. We used a Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test to determine statistical significance (n>7 mice in each experimental group). (C) Giemsa staining of Asxl1+/+; CebpaΔ/p30 or Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaΔ/p30 leukemic blasts isolated from the BM of moribund mice. A normal aged-matched mouse was included as a control. (D) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis of Asxl1+/+; CebpaΔ/p30 or Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaΔ/p30 leukemic blast isolated from transplanted mice. The plot shows the amount of donor-derived c-Kit positive cells. A normal aged-matched mouse was included as a control. (E) Quantification of the data from (D) (n=3 mice in each experimental group).