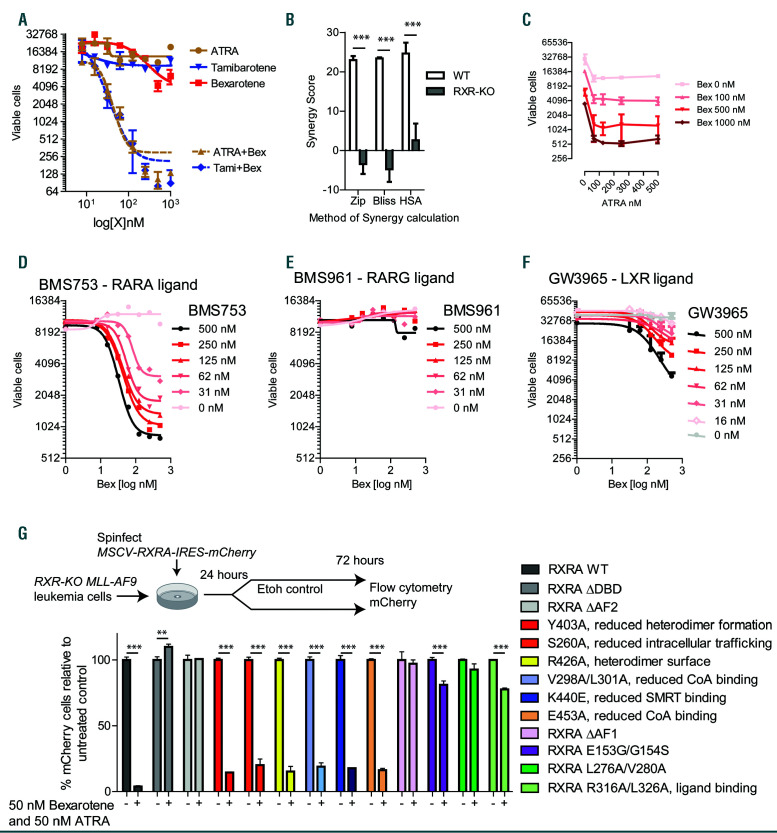
Figure 3.
Pharmacologic targeting of natural retinoic acid receptor (RAR)A and retinoid X receptor (RXR)A ligands blocks MLL-AF9 proliferation in vitro. (A) MLLAF9 leukemia cells derived from UAS-GFP bone marrow (BM) and transduced with MSCV-Flag-Gal4-RXRA-IRES-mCherry retrovirus (MLL-AF9 Gal4-RXRA cells) were treated as indicated, replated after 48 hours (h), and total viable cells in 50 mL assessed in duplicate after 96 total h of treatment at indicated doses. (B) MLL-AF9 RXR-flox (wild-type, WT) or RXR-KO (Rxra/Rxrb deficient) leukemia cells (see Figure 2) were treated with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and bexarotene for 96 total h and the synergy was calculated by SynergyFinder software24 using three different mathematical calculators for synergy versus additive effects (Zip, Bliss, and HAS). In these calculations, results >1 suggest mathematical synergy, although larger values are typically required for biologically relevant synergy. (C) MLL-AF9 Gal4-RXRA cells were treated as indicated, replated after 48 h, and total viable cells in 50 mL were assessed in duplicate after 96 total h of treatment. (D-F) MLL-AF9 leukemia cells were treated as indicated, replated after 48 h, and total viable cells in 50 mL assessed in duplicate after 96 h of total treatment. (G) Rxra/Rxrb deficient MLLAF9 leukemia cells (RXR-KO) were transduced with retrovirus encoding MSCV-RXRA (full length)-IRES-mCherry or retrovirus with indicated RXRA mutations. Mutations and published mutation effects are indicated. 24 h after retroviral transduction, cells were treated in triplicate with 50 nM ATRA/bexarotene, and the proportion of mCherry+ cells was assessed relative to untreated control population after 72 h. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, t-test with Welch’s correction relative to control.