Figure 1.
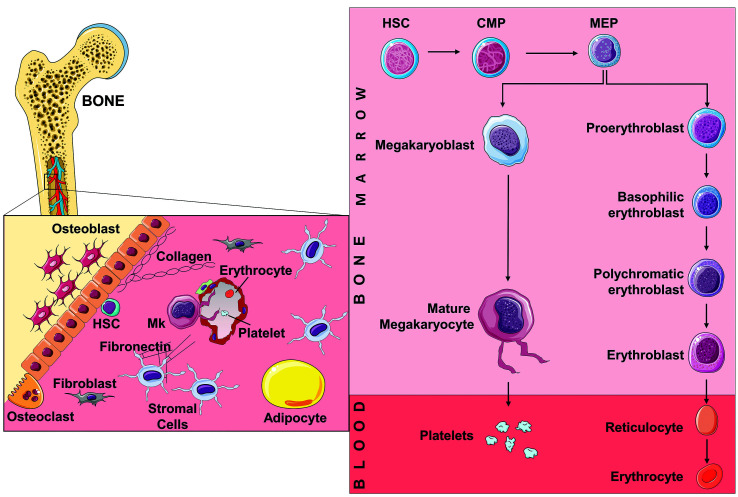
Bone marrow hematopoiesis. Schematic representation of the adult hematopoietic stem cell niche, showing various cell types and extracellular matrix components that influence the differentiation of blood progenitors. The hierarchical differentiation pathways of megakaryopoiesis and erythropoiesis are highlighted. Megakaryopoiesis is typically characterized by an increase in cell size and ploidy, resulting in the final extension of long pseudopods, called proplatelets, which release platelets into the bloodstream. Erythropoiesis entails several morphological and structural changes that give rise to basophilic, polychromatophilic and acidophilic erythroblasts. At the end of the terminal maturation reticulocytes are released into the bloodstream where they complete their maturation into mature erythrocytes. Mk: megakaryocyte; HSC: hematopoietic stem cell; CMP: common myeloid progenitor; MEP: megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor. The figure was created using Servier Medical Art templates licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://smart.servier.com).