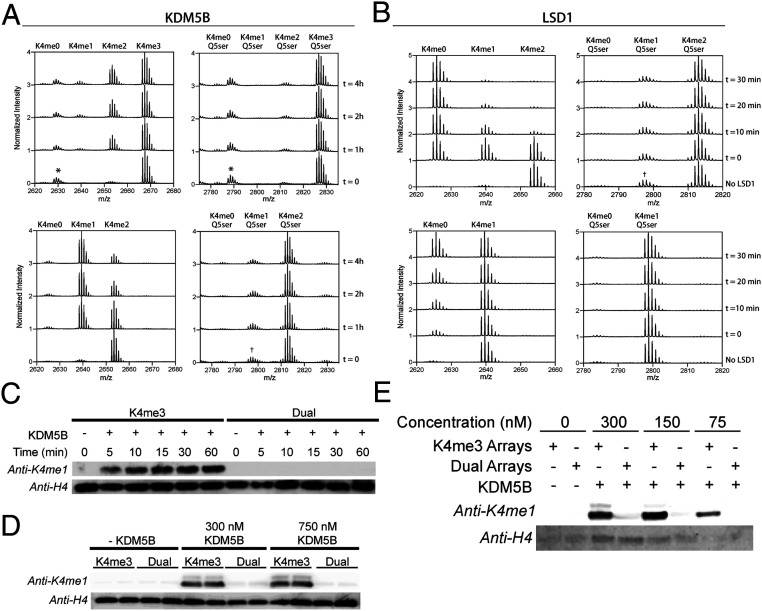
Fig. 3.
Impact of H3Q5ser modification on LSD1 and KDM5B mediated demethylation of H3K4. (A) MALDI-TOF demethylation assay using H3(1–25)K4me3 vs. H3(1–25)K4me3Q5ser peptide substrates (Top) and H3(1–25)K4me2 vs. H3(1–25)K4me2Q5ser peptide substrates (Bottom). Demethylation of H3(1–25)K4me3 resulting in the H3(1–25)K4me1/2 product is visible after 4 h, while no demethylation is observed for H3(1–25)K4me3Q5ser. *Impurity from peptide synthesis. †Residual K4me1Q5ser species from synthesis of K4me2Q5ser substrates, unable to purify. (B) MALDI-TOF demethylation assay as described in A using recombinant LSD1. LSD1 robustly demethylates native substrates K4me2 (Top) and K4me1 (Bottom), while no demethylation activity is seen for substrates containing Q5ser. (C) Western blot of 60-min time course of KDM5B demethylation of 12-mer chromatin array substrates. In the presence of KDM5B, H3K4me3 arrays are readily demethylated, while no demethylation occurs for H3K4me3Q5ser-containing arrays. (D) Western blot of KDM5B concentration course. Increased amounts of KDM5B do not promote demethylation of H3K4me3Q5ser arrays. (E) Increasing 12-mer array substrates in the KDM5B demethylation assay does not promote demethylation of H3K4me3Q5ser arrays.