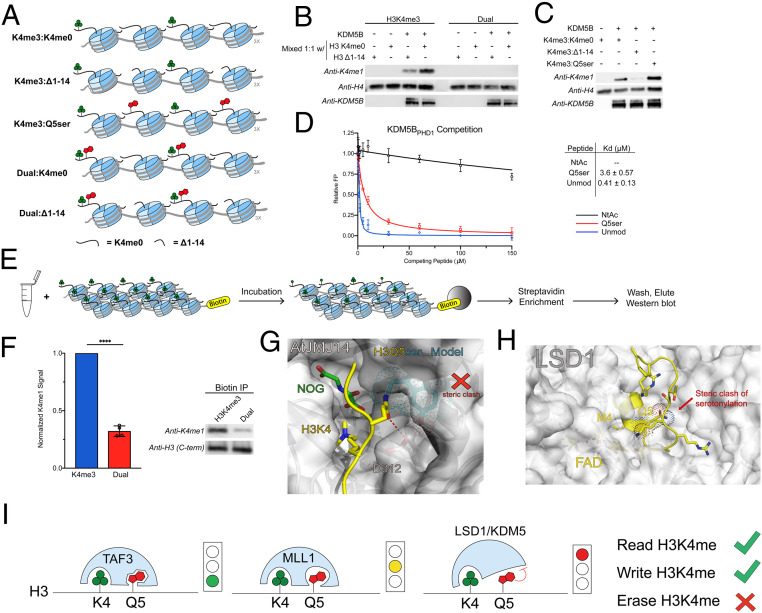
Fig. 4.
KDM5B inhibition of demethylation of semisynthetic 12-mer chromatin arrays. (A) Schematic of mixed 12-mer array substrates. Both H3 tails are modified. (B) H3K4me0 on a neighboring mononucleosome stimulates KDM5B demethylation activity of H3K4me3 but not H3K4me3Q5ser. (C) H3Q5ser on a neighboring mononucleosome does not inhibit stimulation of KDM5B by KDM5BPHD1. (D) Normalized fluorescence polarization of GST-KDM5BPHD1 binding to H3 unmodified (blue) and H3Q5ser (red) peptides. N-terminally acetylated H3 was included as a negative control (black). Errors represent ± SD of n = 3. (E) Experimental flow for chromatin dipping in active, isolated HeLa lysate. (F) Chromatin array dipping in isolated HeLa nuclear lysate followed by streptavidin enrichment shows dramatically less demethylation of H3K4me3Q5ser arrays compared to H3K4me3. Representative Western blot shown from four replicate experiments. t test (two-tailed), 95% confidence; ****, < 0.0001. Errors represent ± SD (G) The catalytic center of JMJ14 (the H3K4me3 eraser in Arabidopsis thaliana) in complex with an H3K4me3 peptide (coordinates were taken from the PDB entry 5YKO). H3K4 and Q5 residues are shown as yellow sticks; the binding surface of JMJ14 is shown as a white surface. The hydrogen bond between H3Q5 and D312 is highlighted with a red dash. Q5ser modification is modeled as cyan sticks. H3Q5ser causes steric clash at the catalytic center of JMJ14. (H) The catalytic center of LSD1 in complex with the histone H3 peptide (coordinates were taken from the PDB entry 2V1D). H3M4 (K4me3 mimic) and Q5 residues are shown as yellow sticks; the binding surface of LSD1 is shown as a white surface. H3Q5ser causes steric clash at the catalytic center of LSD1. (I) Model representing the different degrees of crosstalk between H3K4me3 and H3Q5ser. KDM5/LSD1 are inhibited by Q5ser, MLL1 remains active against Q5ser-modified substrates, albeit with a slower k2, and the reader TAF3 displays increased binding to H3K4me3Q5ser.