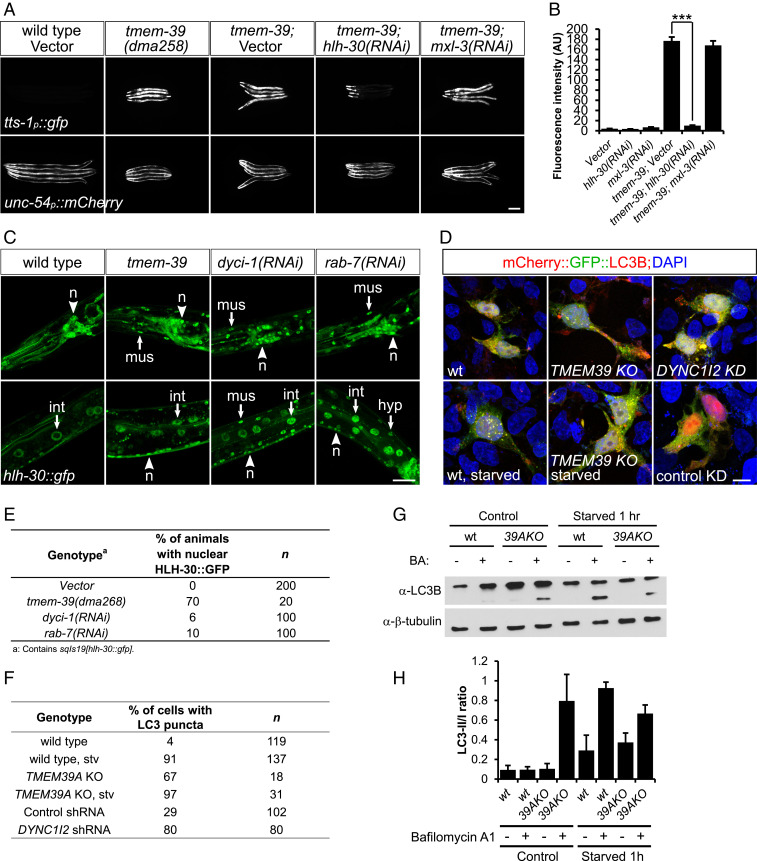
Fig. 3.
TMEM-39 regulates mTOR signaling through the master regulator of lysosome biogenesis HLH-30/TFEB. (A) Expression of an mTOR reporter tts-1p::gfp is strongly up-regulated in tmem-39 mutant animals, while disruption of hlh-30/TFEB by RNAi abolishes tts-1p::gfp up-regulation. unc-54p::mCherry, coinjection reporter; mxl-3, bHLH transcription factor that antagonizes HLH-30 function in lipolysis upon starvation. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (B) Quantification of tts-1p::gfp fluorescence intensity in A. Data represent mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001. AU, arbitrary units. (C) Confocal images showing nuclear localization of HLH-30 in neurons (n), hypoderm (hyp), intestine (int), and muscle (mus) cells of animals deficient in tmem-39, dyci-1, or rab-7, but not in wild type. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (D) Representative confocal images showing puncta formation of mCherry::gfp::LC3 in cells deficient in TMEM39A, DYNC1I2 or following 1 h of starvation. The presence of more red, but not yellow, LC3 puncta in TMEM39A KO cells indicates lysosome-mediated quenching of the GFP signal. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (E) Quantification of HLH-30::GFP nuclear localization in C. (F) Quantification of mCherry::gfp::LC3 puncta formation in D. (G) Western blot analysis showing up-regulation of LC3-II/I ratio in nonstarved TMEM39A KO compared with wild-type HEK 293T cells, indicating enhanced autophagosome formation. BA, bafilomycin A1. (H) Quantification of the Western blot results. Data represent mean ± SEM. wt, wild type.