Figure 3.
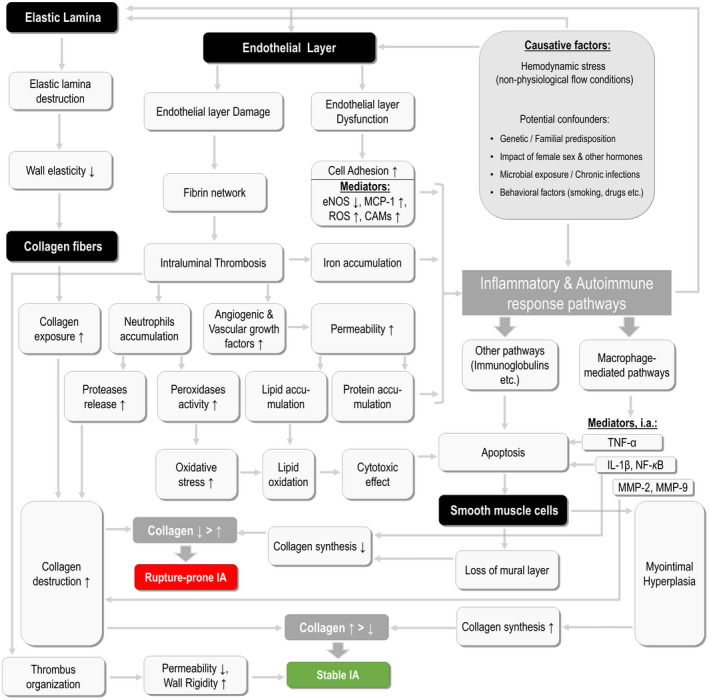
Schematic presentation of the major pathophysiological processes and causative factors involved in intracranial aneurysm (IA) development. This model summarizes the current evidence on the etiologies and consecutive mechanisms leading to IA formation, as well as shows the processes determining the rupture of IA. The anatomic targets within the arterial wall are highlighted with black background, whereat the processes are shown with gray background. Abbreviations: eNOS = endothelial nitric oxide synthase, MCP‐1 = monocyte chemotactic protein 1, ROS = reactive oxygen species, CAMs = cell adhesion molecules, TNF‐α = tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL‐1β = interleukin 1 beta, NF‐kB = nuclear factor kappa b, MMP‐2/‐9 = matrix metalloproteinase‐2/‐9.
