Figure 7.
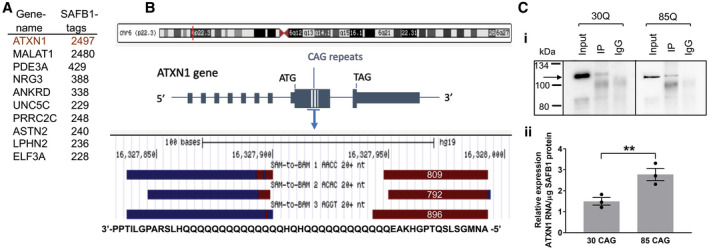
Increased binding of SAFB1 to Ataxin 1 with an expanded glutamine tract. A. The top 10 most SAFB1 bound RNA transcripts with the total number of iCLIP SAFB1 cross‐link sites from three independent experiments. B. The red line depicts the location of the ATXN1 gene on chromosome 6. The majority of the SAFB1 binding sites occur in RNA encoded by exon 8 of ATXN1 and in the region containing CAG repeat sequence (blue hatched lines). A screengrab taken from the genome browser shows the sense (brown) and antisense (blue) SAFB1 iCLIP binding sites. The binding sites relative to the amino‐acids encoded by the SAFB1 bound sequences are shown in a 3′‐5′ orientation. Note the SAFB1 cross‐link site will correspond to the amino‐acid most 5′ to the sense sequence and 3′ to the antisense sequence. The numbers within the schematic of the sense binding sites show the number of SAFB1 cross‐link sites in each of these individual experiments. C i. Western blotting of protein lysates from RNA immunoprecipitation experiments, probed for SAFB1. SAFB1 is present in both ATXN1‐30Q transfected and ATXN1‐85Q transfected cell lysates immunoprecipitated using a SAFB1 antibody (IP). There is no SAFB1 protein detected in IgG control lysates (IgG). Expected molecular weight for SAFB1 is 102KDa (arrow). ii. Relative levels of ATXN1 RNA bound to SAFB1 protein. SAFB1 protein was immunoprecipitated from HeLa cells transfected with plasmids containing ATXN1‐30CAG (physiological) or ATXN1‐85CAG (pathological expansion). The relative expression level of ATXN1 RNA associated with SAFB1 protein is significantly increased in ATXN1‐85 CAG compared to ATXN1‐30 CAG (unpaired, two‐tailed t‐test t(4) = 3.76, P = 0.01). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
