Figure 1.
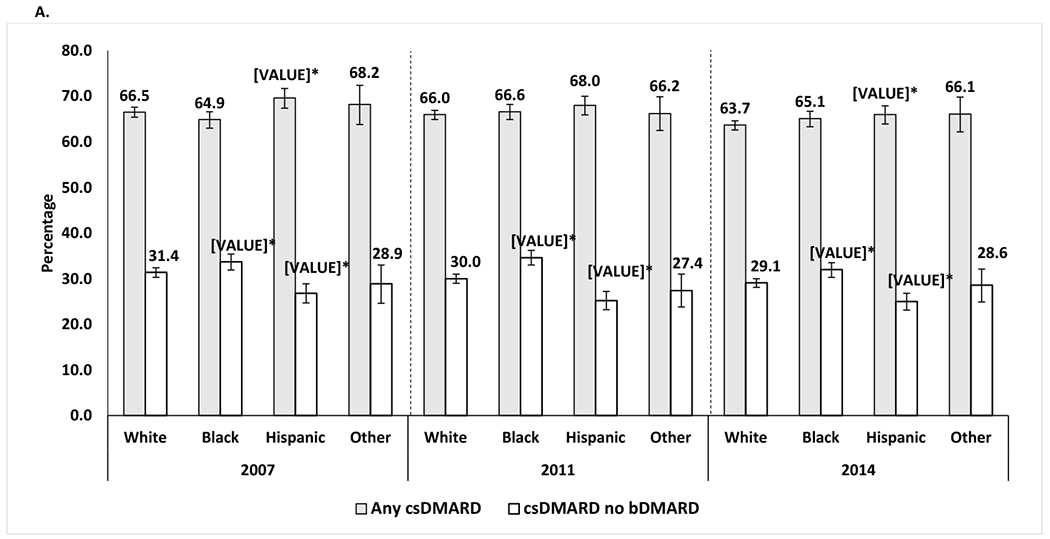
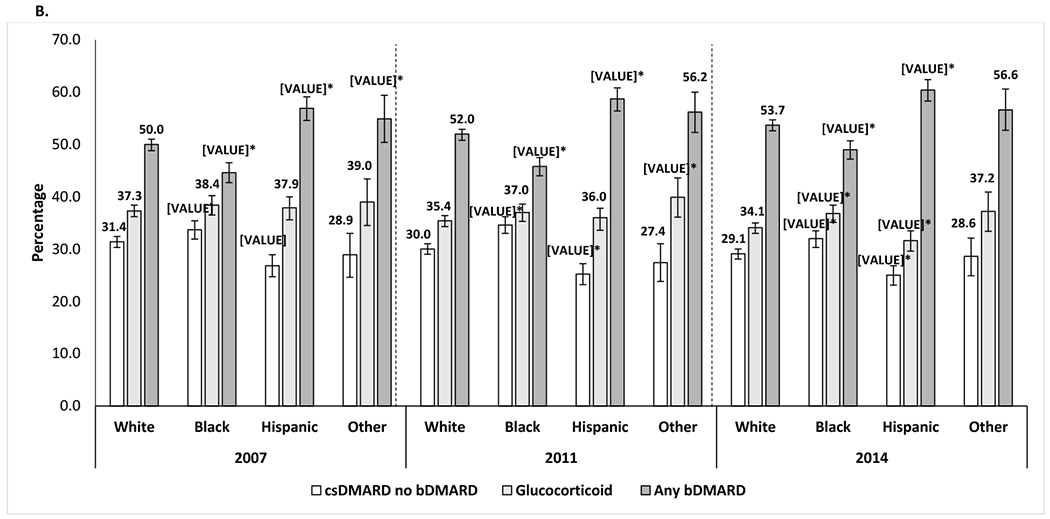
Differences in the use of csDMARD and long-term glucocorticoid by racial/ethnic groups among SSDI beneficiaries with RA who were disabled and younger than 65 years.
Percentage of patients who used csDMARDs with or without bDMARDs among all patients who used csDMARDs in each racial/ethnic group, by year, after adjustment for covariates.
The proportion of patients that were neither on csDMARD, bDMARD or tsDMARD was 18.7% in 2007, 17.9% in 2011 and 17.0% in 2014
*Statistically significant vs. the percentage for White patients
Adjusted for age, sex, Unites States region, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, area deprivation index, fibromyalgia, diabetes, diabetes complications, mental illnesses, transient ischemic attack, stroke or myocardial infarction, and peripheral vascular disease.
Mental illness was defined as any of the following conditions: anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, multiple personality disorder or schizophrenia.
Percentage of all patients among each racial/ethnic group who used csDMARDs without biologics, long-term GCs.¥, or bDMARDs with or without csDMARD, by year, after adjustment for covariates. *, statistically significant vs. the percentage for Whites.
The proportion of patients that were neither on csDMARD, bDMARD or tsDMARD was 18.7% in 2007, 17.9% in 2011 and 17.0% in 2014.
¥Long-term glucocorticoid treatment was defined as an annual cumulative prednisone-equivalent dose of 900 mg or more.
Adjusted for age, sex, United States region, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, area deprivation index, fibromyalgia, diabetes, diabetes complications, mental illnesses, transient ischemic attack, stroke or myocardial infarction, and peripheral vascular disease.
Mental illness was defined as any of the following conditions: anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, multiple personality disorder or schizophrenia.
