Figure 7.
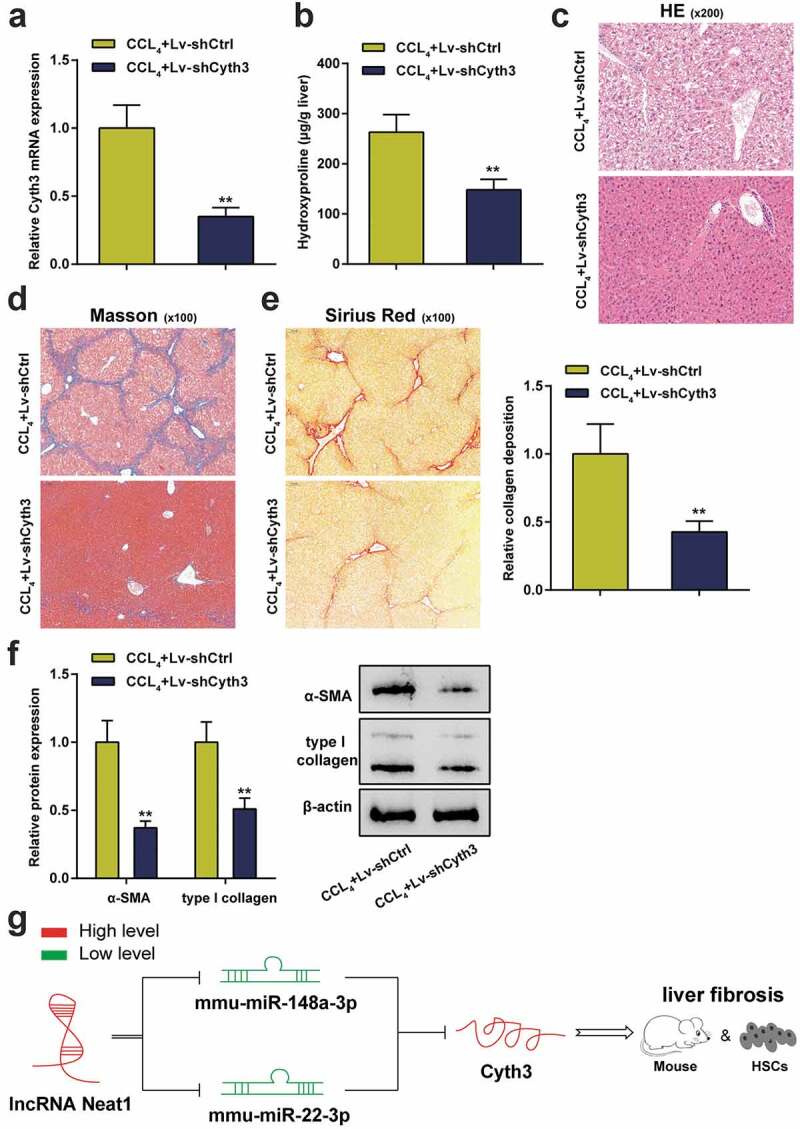
Knockdown of Cyth3 attenuated CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice. Mice were randomized to separate into two groups: (i) the CCl4+ Lv-shCtrl group and (ii) the CCl4+ Lv-shCyth3 group. (a) The expression of the Cyth3 mRNA in different groups was detected using a PCR assay. (b) Quantification of the hepatic hydroxyproline content in different experimental groups. (c) Assessment of tissue damage using H&E staining. (d) Evaluation of liver fibrosis using Masson’s trichrome staining. (e) The degree of liver fibrosis was evaluated by staining tissue sections with Sirius Red. (f) The expression levels of the α-SMA and type I collagen proteins were detected using western blotting. (g) The signaling pathway involved in liver fibrosis was discovered. Schematic representation of a working model by which Neat1 knockdown obstructed Cyth3 expression by regulating miR-148a-3p and miR-22-3p to participate in liver fibrosis and HSC activation N = 6; **P< 0.01, compared with CCl4+ Lv-shCtrl
