Figure 3.
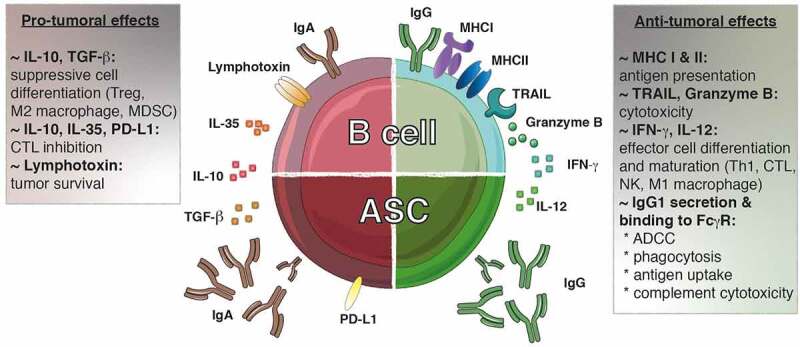
The dichotomy of tumor-infiltrating B lymphocytes. Both pro- and anti-tumoral roles can be attributed to B lymphocytes. IgG1+ B cells promote the anti-tumoral response by presenting antigens to T cells and secreting cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-12) that polarizing the response toward an optimal Th1/CTL composition. These B cells can exert direct cytotoxic functions through the expression of TRAIL and granzyme B. Furthermore, the IgG1 antibodies secreted by the ASC can bind to the FcγR at the surface of NK cells, macrophages and dendritic cells allowing induction of ADCC, phagocytosis and antigen uptake, respectively. Furthermore, IgG1 antibodies fix complement to trigger its cytotoxic cascade. In contrast, IgA+ cells are associated with the secretion of inhibitory cytokines (IL-10, IL-35, TGF-β) that create a suppressive environment favoring the emergence of Treg, M2 macrophages and MDSC while repressing the function of the effector cells. In addition, the expression of lymphotoxin by B cells supports tumor cell survival. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; ASC, antibody secreting cell; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; FcγR, Fc gamma receptor; Ig, immunoglobulin; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MHC: major histocompatibility complex; PD-L1: progammed cell death ligand 1; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; TRAIL, tumor-necrosis-factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Treg, regulatory T cell
