Fig. 10.
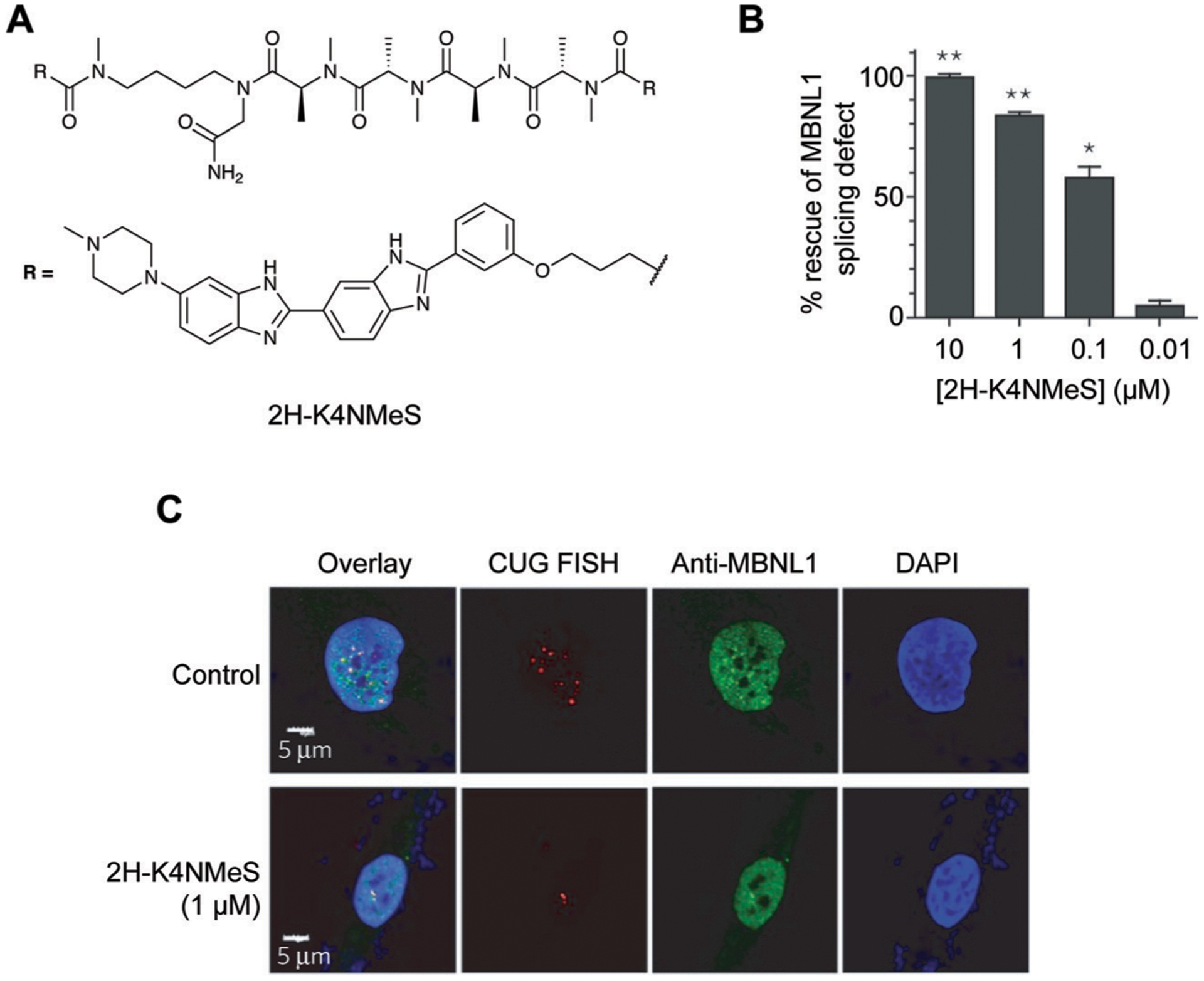
Targeting CUG repeat expansions with a multivalent ligand in DM1. (A) Structure of 2H-K4NMeS. (B) 2H-K4NMeS treatment reduces CUG:MBNL1 foci. RNA was detected with Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH), where fluorescently-labeled oligonucleotides complementary to an RNA of interest are incubated in cells to show their subcellular localization. Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). Adapted from ref. 10 with permission from Springer Nature, Copyright 2016. MBNL1 was detected using immunofluorescence, where a fluorescently-labeled antibody for MBNL1 was incubated in cells to show its subcellular localization. White regions in the “Overlay” show where FISH, MBNL1, and DAPI signals overlap. (C) Treatment with 2H-K4NMeS shows dose-dependent rescue of MBNL1 splicing defect. Adapted from ref. 10 with permission from Springer Nature, Copyright 2016.
