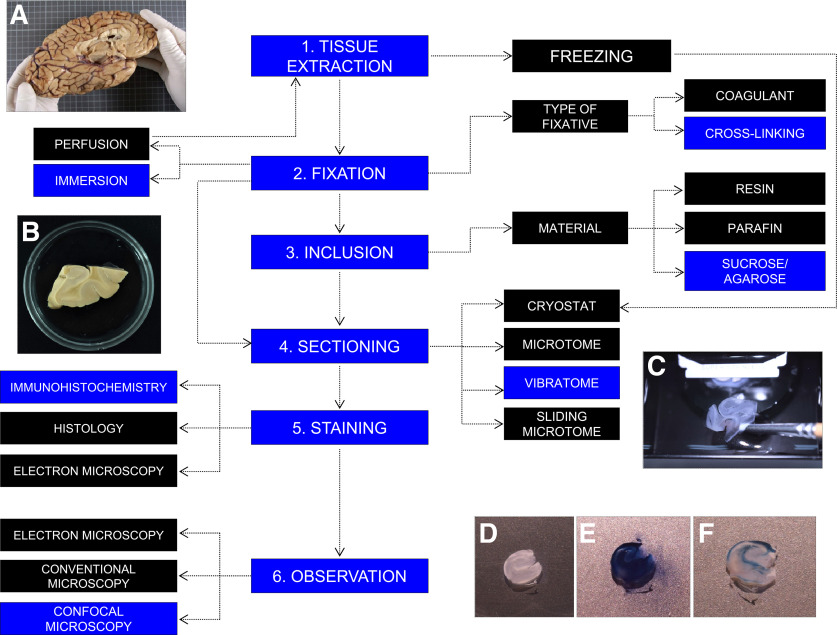
Figure 1.
Variety of methods routinely used to process postmortem human brain samples. During autopsy, the brain is removed from the skull (A). After dissecting the area of interest, tissue can be either frozen or fixed. Various chemical fixatives can be used. After fixation, samples can be embedded in resin, paraffin, or a mixture of agarose/sucrose (B) to favor tissue preservation and sectioning. Depending on the embedding support, a cryostat, microtome, or vibratome (C) sectioning method should be used. Staining is performed following previously established immunohistochemical, histologic, or electron immunohistochemical protocols. Human hippocampal sections subjected to immunohistochemistry staining before (D), during (E), and after (F) the final autofluorescence elimination step are shown. Stained sections can be observed under conventional epifluorescence, electron, or confocal microscopes. Blue represents the protocol followed in our laboratory. A complete description of this protocol can be found in Moreno-Jiménez et al. (2019) and Flor-García et al. (2020).