Figure 2.
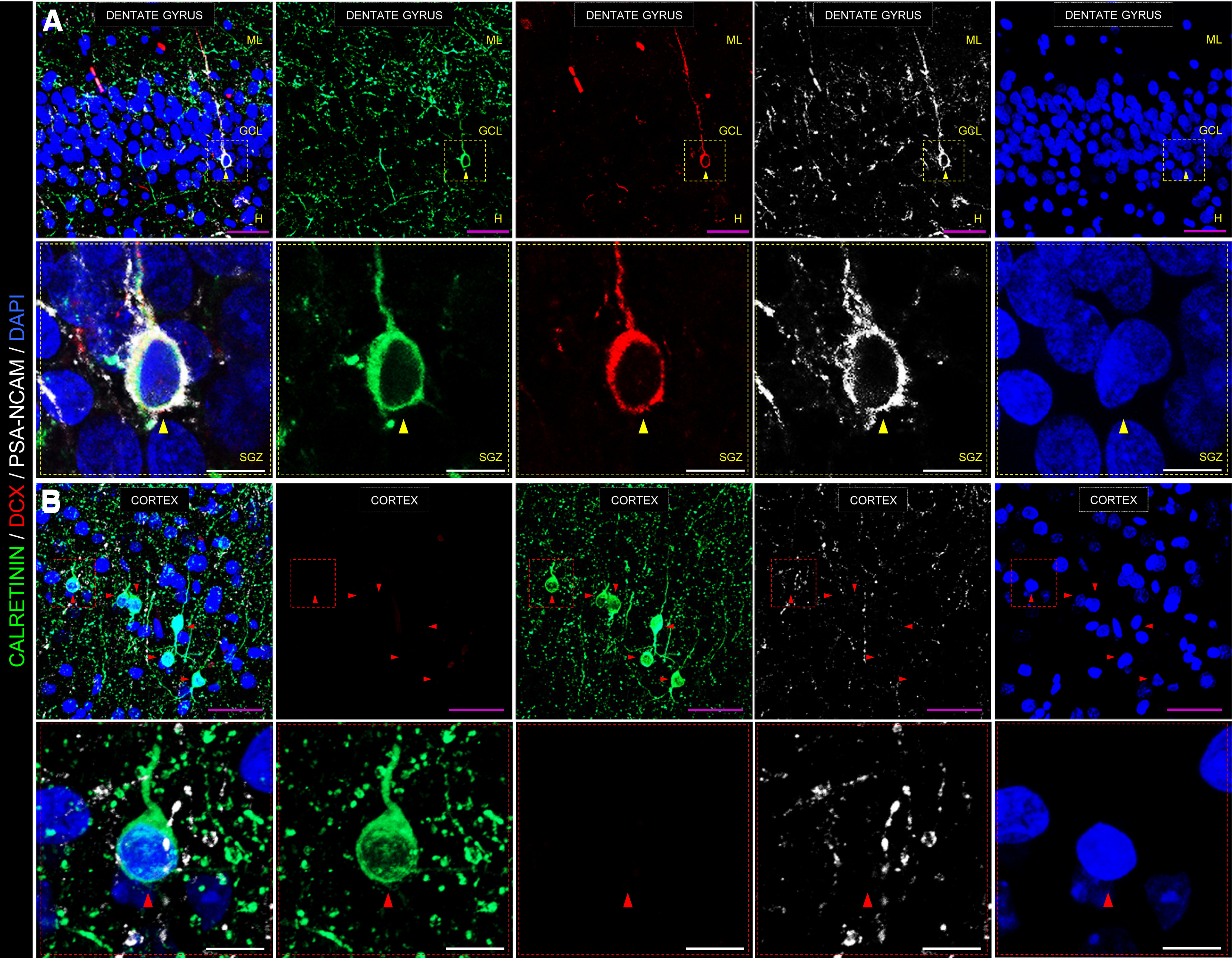
Representative images showing an immunohistochemical staining performed on postmortem human hippocampal samples. A, Low- and high-power magnification images show the anatomic organization of the human DG. In high-power magnification images, a triple-labeled DCX+/calretinin+/PSA-NCAM+ immature dentate granule cell is shown. B, Representative image of the human cortex is shown as a negative control for DCX staining. Note the abundance of calretinin+ interneurons, which is in sharp contrast to the absence of DCX+ cells in this structure. GCL, Granule cell layer; ML, molecular layer; H, hilus; SGZ, subgranular zone. Scale bars: magenta, 50 μm; white, 10 μm. Yellow triangles represent DCX+/calretinin+/PSA-NCAM+ immature dentate granule cell. Red triangles represent DCX–/calretinin+/PSA-NCAM– cortical interneuron. Immunohistochemistry was performed following a previously published protocol (Moreno-Jiménez et al., 2019; Flor-García et al., 2020), which included sodium borohydride (NaBH4), heat-mediated citrate antigen retrieval (HC-AR), and autofluorescence elimination steps. Low-power confocal stacks of images were obtained in a LSM800 Carl Zeiss confocal microscope, equipped with three GaAsP detectors and using a 40× immersion oil objective. A, 0.8 zoom, XY dimensions: 199.66 µm, Z interval: 1.5 µm, pinhole dimensions: 0.9 Airy units. B, 1.1 zoom, XY dimensions: 145.2 µm, Z interval: 1.5 µm, pinhole dimensions: 0.9 Airy units. High-power magnification images were obtained in the same confocal microscope using a 63× immersion oil objective (2.2 zoom, XY dimensions: 46 µm, Z interval: 0.5 µm, pinhole dimensions: 0.9 Airy units). All the images shown in this figure correspond to postmortem human samples obtained from a neurologically healthy control subject. Fixation time was limited to 24 h in freshly prepared 4% PFA at 4°C. The epidemiological data of this subject are the following: gender, male; age, 43; postmortem delay, 5 h; Braak-Tau stage, 0; CERAD stage, 0; and Braak α-synuclein stage, 0. Brain tissue donation, processing, and use for research were in compliance with published protocols (Martinez-Martin et al., 2010), which include the obtaining of informed consent for brain tissue donation from living donors, and approval of the whole donation process by the Ethical Committee of the Spanish Research Council (Committee Approval Reference 025-2020#).
