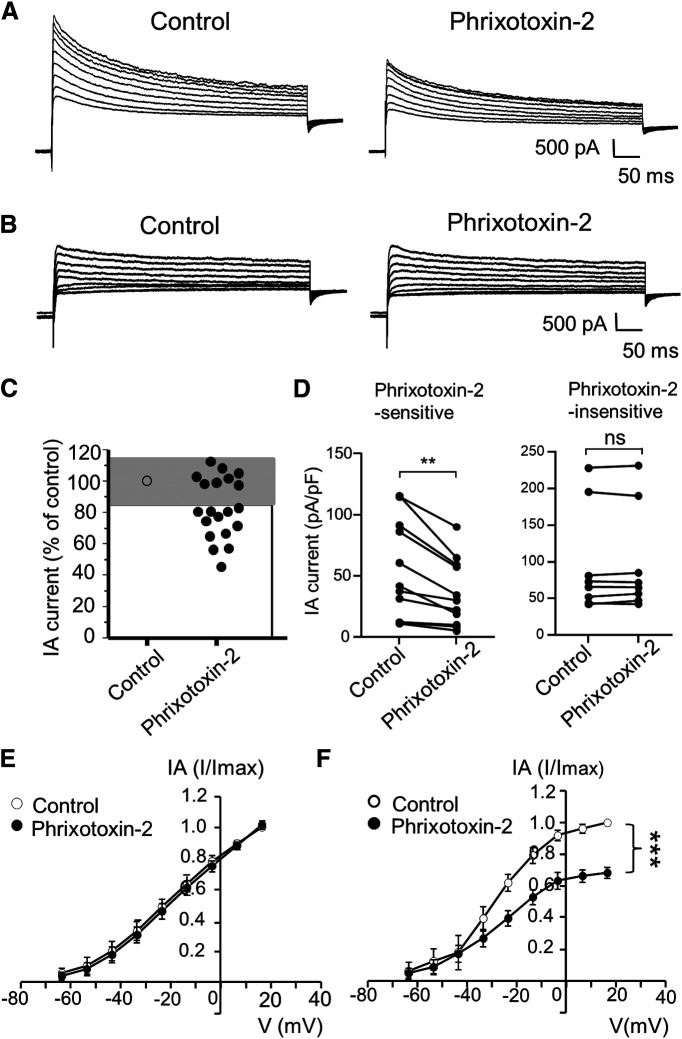
Figure 8.
Kv4.3 blocker phrixotoxin-2 inhibits IA currents in small-sized V2 TG neurons. A, Sample traces show isolated IA currents in a small-sized V2 TG neuron before (control, left) and following the application of 70 nm phrixotoxin-2 (right). B, Sample traces show isolated IA currents in another small-sized V2 TG neuron before (control, left) and following the application of 70 nm phrixotoxin-2 (right). C, Graph shows changes of IA currents following the application of phrixotoxin-2. IA currents following phrixotoxin-2 were scaled to control values (% of control). Cells whose IA currents showed changes less than ±15% (gray area) were considered to be phrixotoxin-2-insensitive (n = 8); cells whose IA currents showed the reduction >15% (white area) were considered to be phrixotoxin-2-sensitive (n = 12). D, Pooled data of IA currents before (control) and following the bath application of 70 nm phrixotoxin-2. Left panel, Recordings from phrixotoxin-2-sensitive (n = 12) small-sized V2 TG neurons. Right panel, Recordings from phrixotoxin-2-insensitive (n = 8) small-sized V2 TG neurons. In both C, D, IA currents were evoked by a voltage step from −63.6 to 6.4 mV, and their mean values in the control and following the phrixotoxin-2 application were used for the statistical comparison. E, F, I-V curves of isolated IA currents before (control, open circles) and following the application of phrixotoxin-2 (closed circles) in the phrixotoxin-2-insenstive group (left, n = 8) and phrixotoxin-2-sensitive group (right, n = 12). In E, F, IA current of each voltage point was normalized to the maximal current in control, and areas under the curves in the control and following the phrixotoxin-2 application were used for the statistical comparison. Data represent mean ± SEM; NS, no significant difference; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.