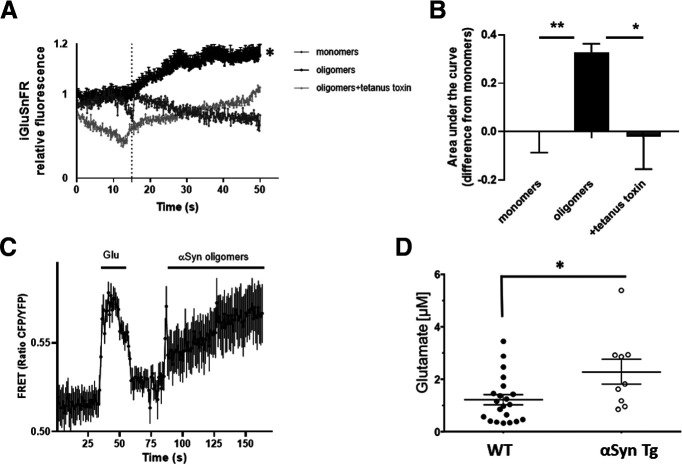
Figure 2.
Oligomeric αSyn induces glutamate release in mouse astrocytes. A, Fluorescent sensor iGluSnFR detected an increase in glutamate following exposure of astrocytes to oligomeric αSyn but not monomers; the increase in glutamate was blocked by tetanus toxin. Dotted line indicates time of addition of αSyn. B, Quantification of glutamate levels measured as area under the curve (n = 7 biological replicates in separate experiments). C, The glutamate sensor SuperGluSnFR, using FRET ratio to monitor glutamate levels after oligomeric αSyn exposure, revealed similar results (n = 7). D, Quantification of microdialysis from mouse brain showing glutamate levels in WT (n = 21) and αSyn transgenic (n = 9) animals. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test for multiple comparisons or a Student's t test for comparison of two groups.