Figure 5.
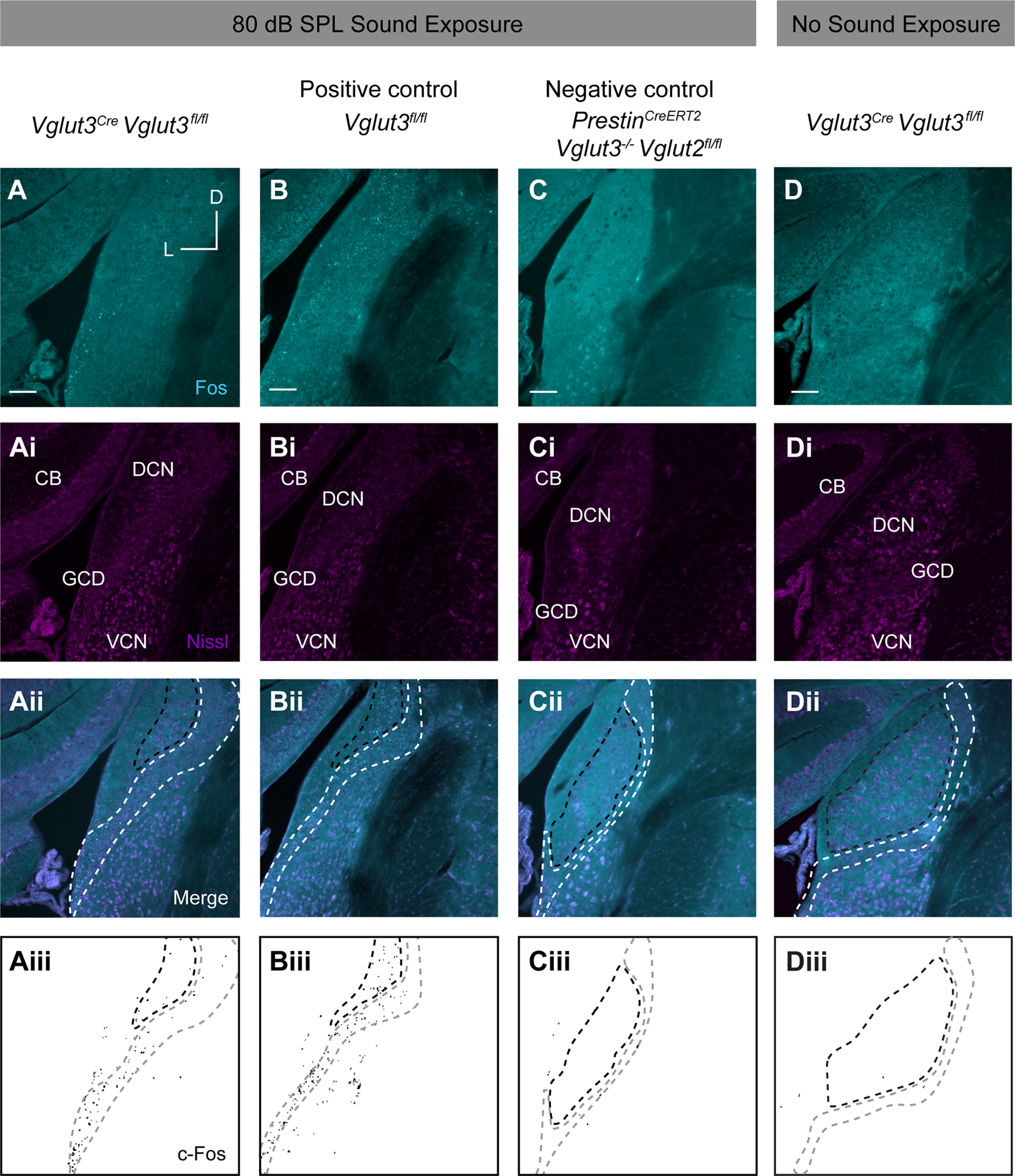
Sound-induced expression of c-Fos in the CN in response to a moderate nondamaging, 80 dB SPL, level of sound, or to no sound stimulus. A, Representative images from Vglut3Cre;Vglut3fl/fl mouse following sound exposure show c-Fos immunoreactivity (cyan) restricted to the GCD. Ai, Nissl staining (magenta). Aii, Merge of cyan and magenta channels. CB, Cerebellum. Aiii, Mask of c-Fos signal from A. Aii-Dii, Region enclosed by white dashed line indicates GCD. Region enclosed by black dashed line indicates regions of the DCN that also contain granule cells. B, Representative image of the CN of Vglut3fl/fl (positive control) mouse subjected to 80 dB SPL sound exposure shows c-Fos immunoreactivity (cyan) throughout DCN and GCD. Bi, Nissl staining of cell somata (magenta). Bii, Merge of cyan and magenta channels. Biii, Mask of c-Fos signal from B. C, Representative image from PrestinCreERT2;Vglut3−/−;Vglut2fl/fl negative control mouse following sound exposure indicates background levels of c-Fos immunoreactivity (cyan). Ci, Nissl staining (magenta). Cii, Merge of cyan and magenta channels. Ciii, Mask of c-Fos signal from C. D, Representative image from Vglut3Cre;Vglut3fl/fl mouse that was not exposed to sound indicates background levels of c-Fos immunoreactivity (cyan). Di, Nissl staining (magenta). Dii, Merge of cyan and magenta channels. Diii, Mask of c-Fos signal from D. Scale bars, 100 µm.
