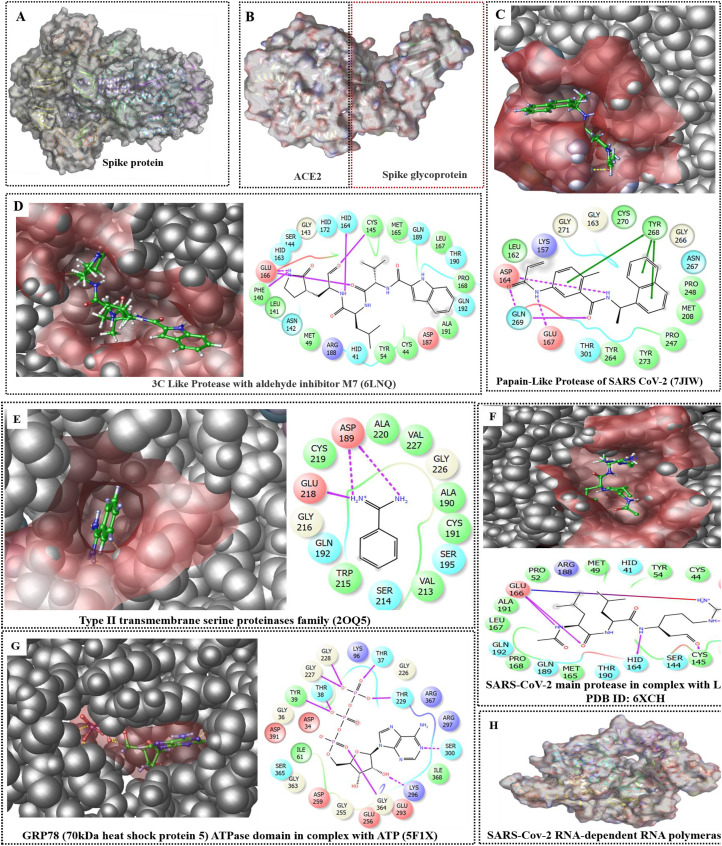
Fig. 3.
(A–H). Pictorial representation of key druggable targets involving both host and virus protein explored for identifying lead molecules using various drug design approaches. Herein, A represents the 3D structure of the spike protein, whereas B represents the binding pattern of viral spike protein with the ACE-2 receptor of the host cells. The interaction of spike protein with host ACE2 protein is critical. It facilitates the viral genome's entry within the host cell and helps in viral propagation and so, the Covid-19 disease. Therefore, designing molecules to prevent spike-ACE2 interaction seems to be a valuable strategy to prevent the propagation of the Covid-19 disease. C represents the papain-like protease of SARS-CoV-2, whereas the co-crystallized ligand's position represents one of the protein's druggable cavity. For the same protein, a 2D protein-ligand interaction profile was also provided, and it represents the critical amino acid residues involved there. Similarly, the druggable cavities of the other essential target proteins viz (D) 3CLPro, (E) type II transmembrane serine proteases, (F) main protease with leupeptin, (G) GRP78 ATPase domain, along with its 3D and 2D protein-ligand interaction profile was provided here. Finally, the 3D structural features of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (H) are also provided. All these proteins are important targets for developing drugs against SARS-CoV-2 infection to combat Covid-19 disease.