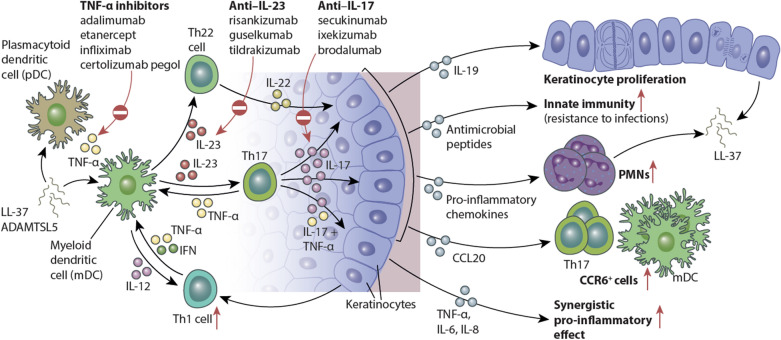
Fig. 1.
IL-23/IL-17–mediated effects on epidermal keratinocytes in psoriatic skin. Schematic showing the broad downstream effects of increased IL-23 and IL-17 signaling on various immune cell populations and keratinocyte biology. Regulated by IL-23, the primary effects of IL-17 on keratinocytes include the following: indirect induction of epidermal hyperplasia through cytokines such as IL-19; upregulation of the innate immune response and antimicrobial peptides; epidermal recruitment of leukocyte subsets through increased production of keratinocyte-derived chemokines; and transcription of multiple pro-inflammatory genes that act synergistically with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α to sustain the inflammatory events in psoriatic skin. PMN polymorphonuclear leukocyte; Th T helper.
Adapted from Hawkes JE, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140(3):645–653. Copyright 2017, with permission from Elsevier