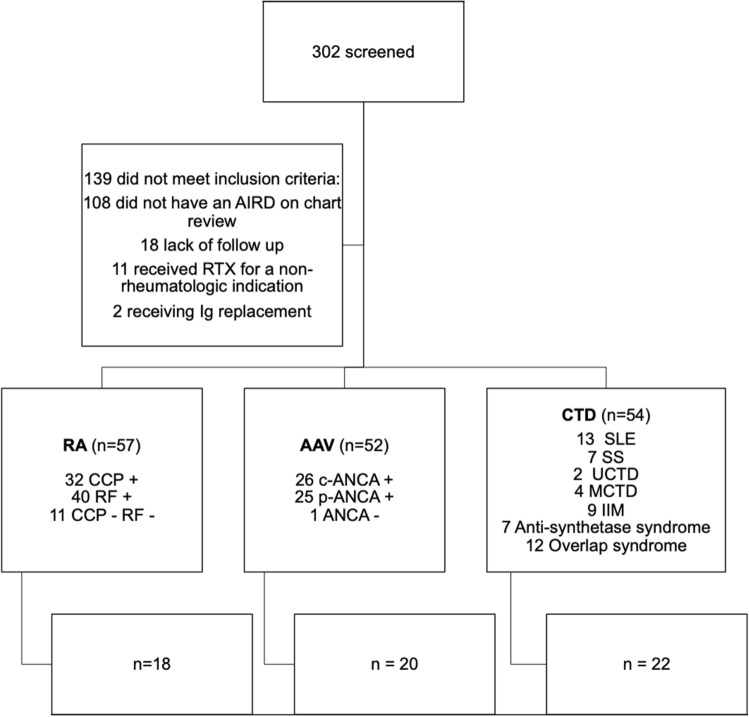
Fig. 1.
Patients with AIRD treated with rituximab were included in the study. We excluded patients without a well-established diagnosis of AAV, RA, or CTD, after comprehensive chart review, those without follow-up at our center, those who received RTX for a non-rheumatologic indication, and those who received concomitant Ig replacement for the treatment of their underlying disease (second row). Of the remaining patients, we analyzed those who had IgG measurements before and after rituximab treatment (fourth row); however, we reported on infections for the whole cohort (third row). AIRD autoimmune rheumatic disease, AAV anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, C-ANCA cytoplasmic-ANCA, CCP cyclic citrullinated peptide, CTD connective tissue disease, IIM idiopathic inflammatory myopathy, Ig immunoglobulin, MCTD mixed connective tissue disease, P-ANCA perinuclear-ANCA, RA rheumatoid arthritis, RF rheumatoid factor, SLE systemic lupus erythematosus, SS Sjogren’s syndrome, UCTD undifferentiated connective tissue disease