Fig. 1.
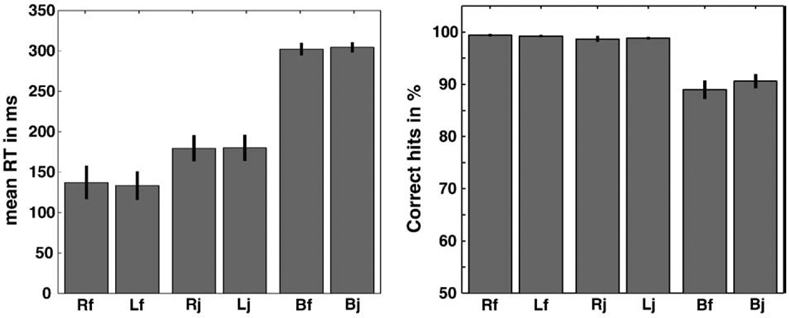
Left panel: Mean reaction times for the six experimental conditions. In the unilateral conditions, uncertainty in timing results in significant slower reaction times. Uncertainty of the response type also produced significant slower reaction times. Comparing fixed and jittered presentation of randomly pointing arrows, however, we observed no significant differences in reaction time. Right panel: Mean percentages of correct responses for the six experimental conditions. A significant main effect was only found for response type uncertainty.
