FIGURE 4.
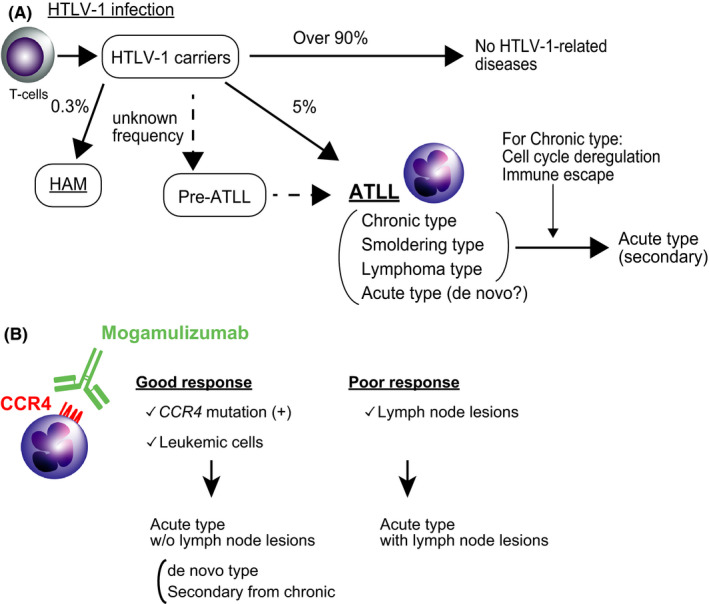
Progression patterns of HTLV‐1–related diseases. A, HTLV‐1 infection is considered to be an initial disease “hit.” The majority of HTLV‐1 carriers do not develop any related diseases. Individuals at pre‐ATLL stage do not experience any symptoms, but ATLL‐related mutations exist. Although it is known that approximately 5% of carriers develop ATLL, it is unclear what percentages of the carries with pre‐ATLL develop ATLL. Some HTLV‐1 carriers develop acute‐type ATLL with intervention from other subtypes of ATLL (secondary). They may also directly develop acute‐type ATLL (de novo). HTLV‐1, human T‐cell lymphotropic virus type 1; ATLL, adult T‐cell leukemia/lymphoma; HAM, HTLV‐1–associated myelopathy. B, Possible differences of response to mogamulizumab in ATLL cases. Presence of CCR4 mutation and the location of tumor cells have been currently identified as markers for response to mogamulizumab. Collectively, among acute‐type ATLL, the cases having CCR4 mutation without lymph node lesions are suspected to have good response to mogamulizumab. The cases with lymph node lesions may have poor response to mogamulizumab
