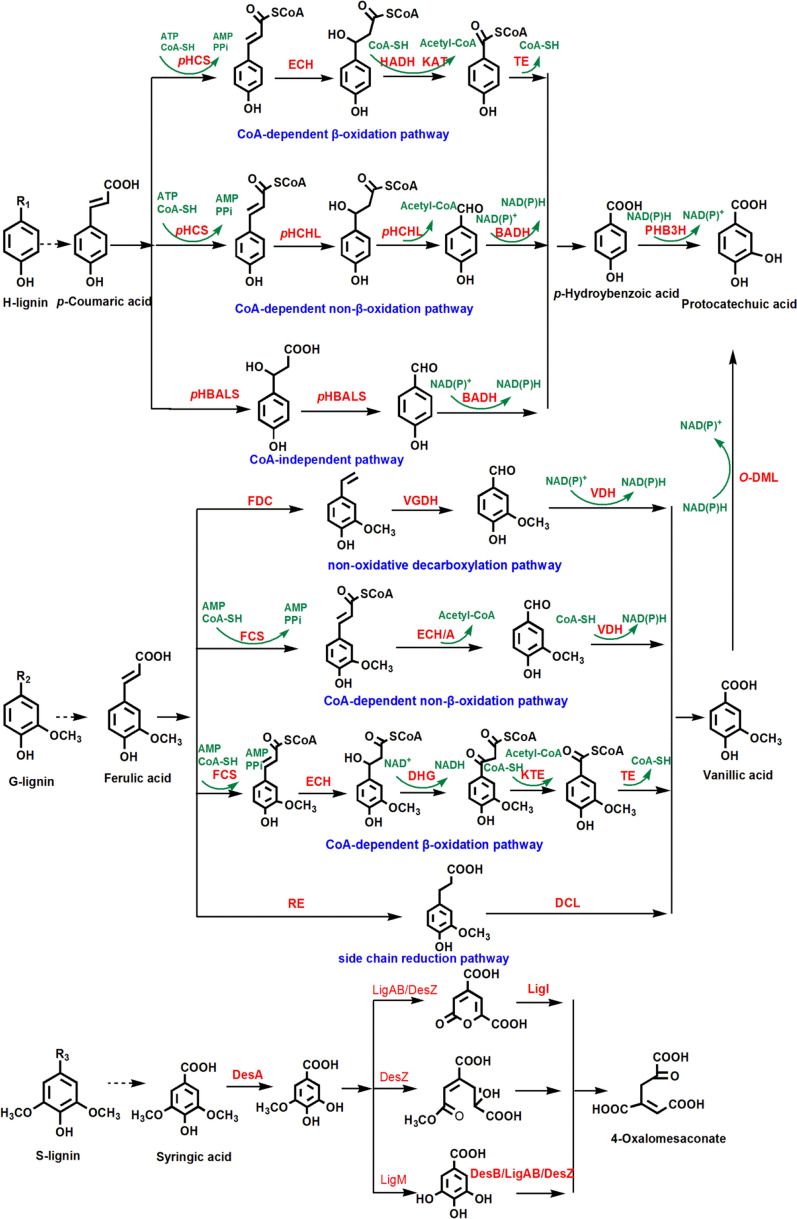
Fig. 6.
Degradation pathways for lignin-based aromatic compounds. H-lignin (p-coumaric acid) can be degraded to protocatechuic acid through three different pathways: CoA-independent pathway, CoA-dependent non-β-oxidation pathway, and CoA dependent β-oxidation pathway [111]. The degradation pathway of G-lignin (ferulic acid) can be divided into non-oxidative decarboxylation pathway, CoA-dependent non-β-oxidation pathway, CoA-dependent β-oxidation pathway, and side chain reduction pathway [118]. These four pathways are all transformed into vanillic acid involved with different intermediates and enzymes. S-lignin (syringic acid) is assimilated into 4-oxalomesaconate derived from the protocatechuic acid 4, 5-cleavage pathway via a series of enzyme reactions [120]