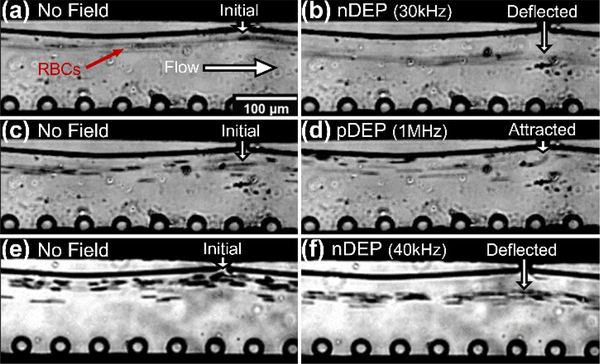
Figure 6:
Dielectrophoretic (DEP) deflection of h-RBCs: (a) before (0.24 μL/min sample flow) versus (b) after nDEP deflection initiated by 80 Vpp at 30 kHz, for cells in buffer of 280 μs/cm media conductivity, to cause net displacement of ~30 μm from the original sample streamline; (c) before (0.24 μL/min sample flow) versus (d) after pDEP deflection initiated by 80 Vpp at 1 MHz, for cells in buffer of 280 μs/cm media conductivity, to cause net displacement of ~10 μm from the original sample streamline. The ability to cause nDEP at even higher sample flow rates (12 μL/min) is apparent from images before (e) versus after nDEP (f), using 100 Vpp at 40 kHz to displace RBCs in buffer of 570 μs/cm media conductivity to ~30 μm from the original sample streamline (video in ESI).