Figure 8.
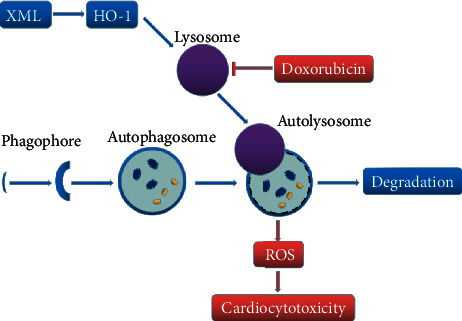
Graphical diagram representing the protective mechanism of XML against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in H9c2 cells. Doxorubicin inhibits lysosomal function and blocks cardiomyocyte autophagy flux. Accumulation of autolysosomes increases ROS production and cell damage. XML rescues lysosomal function by increasing HO-1, then promotes autophagy flux and decreases the accumulation of autolysosomes, and finally reduces ROS and cell oxidative stress damage.
