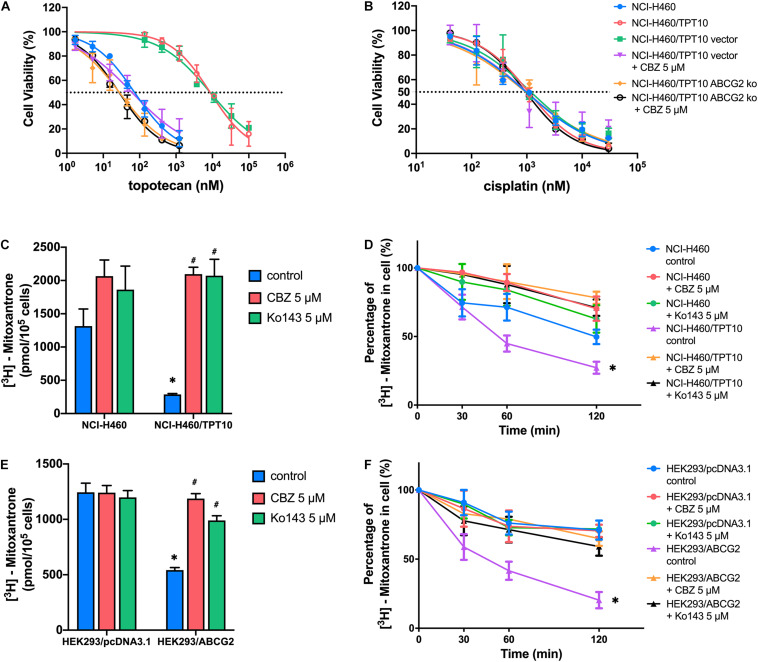
FIGURE 2.
ABCG2 inhibition as a major mechanism for the reversal activity of cabozantinib. (A,B) Cell viability was determined by MTT assay and displayed the changes in response to different concentrations of topotecan (A) or cisplatin (B) with the presence of 5 μM cabozantinib in NCI-H460, NCI-H460/TPT10, the ABCG2 gene knockout subline of NCI-H460/TPT10, and the vector-transfected cells. Data points with error bars represented the mean viability (%) ±SD of at least three independent experiments, each done in triplicate. (C,E) The effect of cabozantinib on the cellular accumulation of [3H]-mitoxantrone in H460, H460/TPT10, HEK293/pcDNA3.1, and HEK293/ABCG2 cells. ∗indicates p < 0.05 comparing resistant cell line to parental cell line with the same treatment; #indicates p < 0.05 comparing a group with cabozantinib to the corresponding cell line group without ABCG2 inhibitor. Ko143 was used as a positive control of ABCG2 inhibition. (D,F) The effect of cabozantinib on the efflux activity of ABCG2 H460, H460/TPT10, HEK293/pcDNA3.1, and HEK293/ABCG2 cells. Data points with error bars represented the mean ± SD of three independent experiments in triplicate. ∗indicates p < 0.05 compared to NCI-H460 control group or HEK293 control group.