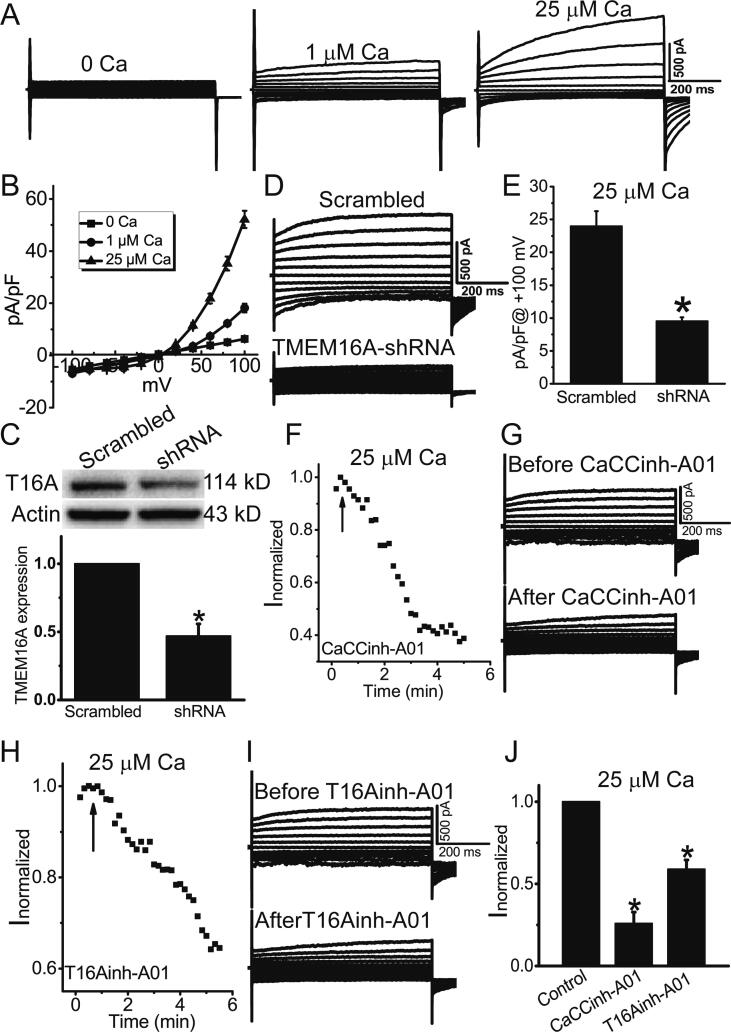
Fig. 1.
TMEM16A mediated Ca2+-activated Cl− currents in HAECs. A. Representative whole-cell Cl− currents activated by different Ca2+ concentrations (0, 1, and 25 μM). The currents were elicited with 750-ms voltage steps from –100 mV to + 100 mV in 20 mV increments. B. The current–voltage relationship of Cl− currents activated by 0, 1, and 25 μM Ca2+. n = 4–5 cells. C. Western blot results of TMEM16A expression in HAECs treated with scrambled shRNAs and TMEM16A-shRNAs. n = 3. *p < 0.05 vs scrambled shRNA. D. Representative whole-cell Cl− currents activated by 25 μM Ca2+ in HAECs treated with scrambled shRNAs and TMEM16A-shRNAs. E. Mean current densities at + 100 mV in D. n = 5–6 cells. *p < 0.05 vs scrambled shRNA. F. H. The time course of Cl− currents activated by 25 μM Ca2+ in cells treated with the TMEM16A inhibitors CaCCinh-A01 (20 μM) (F) or T16Ainh-A01 (20 μM) (H). Cells were clamped from ramps from − 100 to + 100 mV with a 750-ms duration at 10 s intervals. The current was normalized to the peak current before CaCCinh-A01 or T16Ainh-A01 application. The application of CaCCinh-A01 or T16Ainh-A01 is indicated by the arrow. G. I. Representative current traces before (top) and after (bottom) CaCCinh-A01 (G) or T16Ainh-A01 (I) treatment. J. The normalized currents (Inormalized) before and after CaCCinh-A01 or T16Ainh-A01. The currents were normalized to those before application of these inhibitors. n = 4–6 cells. *p < 0.05 vs control (before treatment).