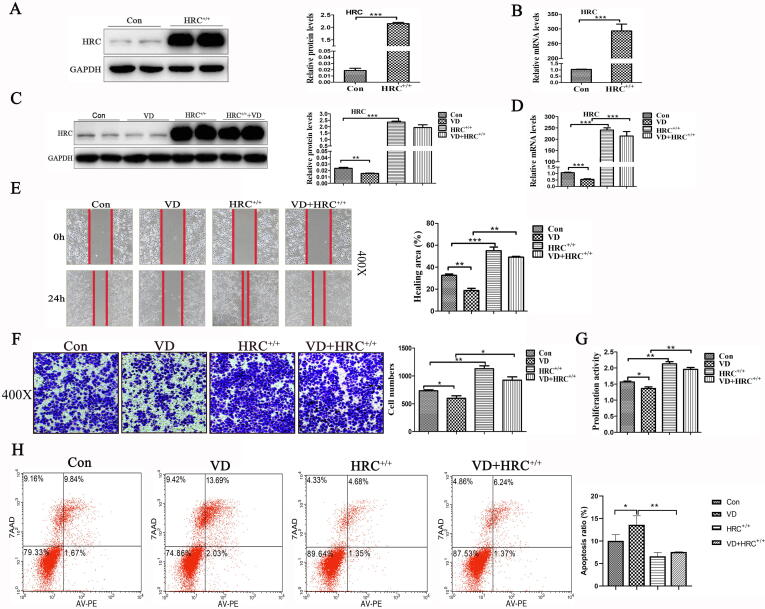
Fig. 4.
HRC+/+ attenuated the effects of vitamin D on cell migration, proliferation and apoptosis. (A) Western blots show HRC overexpression in H460 cells; a 200-fold increase in HRC expression was noted. (B) Overexpressed HRC detected by real time RT-PCR. (C) The histogram shows HRC protein expression after 24 h incubation with vitamin D. (D) Effects of vitamin D on HRC mRNA expression determined by real time RT-PCR. (E) Wound healing assay. Vitamin D with HRC+/+ partially reduced cell mobility compared with that with HRC+/+, but the effect was weaker than that in the VD group. (F) Transwell migration assays. The histogram shows that vitamin D with HRC+/+ partially inhibited H460 cell migration. (G) Assays of H460 cell proliferation showed that HRC+/+ attenuates the effects of vitamin D on cell migration and proliferation. (H) Apoptosis induction assessed by flow cytometry after staining with annexin V-PE/7-AAD. Vitamin D-induced H460 cell apoptosis was significantly reduced by HRC+/+. Values are expressed as means ± SD. Statistical significance is shown as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. HRC, Histidine-rich calcium binding protein.