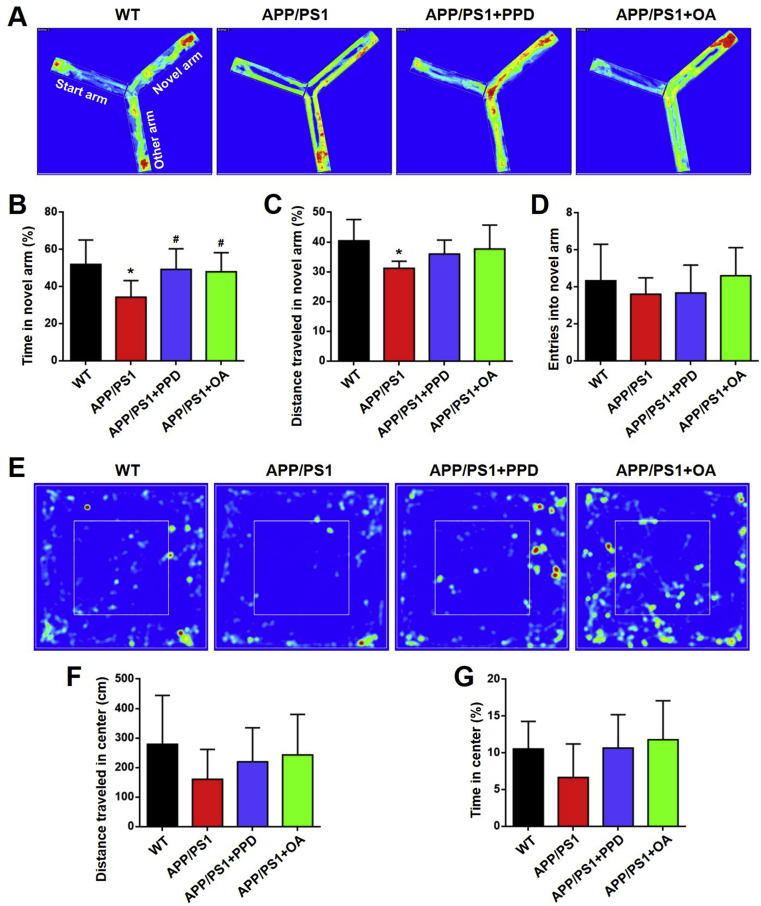
Fig. 2.
PPD or OA administration enhances the performance in the Y maze and open field test by APP/PS1 mice. (A-D) The Y maze test for WT mice, APP/PS1 mice, and APP/PS1 mice treated with PPD or OA. (A) Representative occupancy plots showing the areas in which the mice spent the most time during the Y maze test. (B) The percentage of time spent in the novel arm of the Y maze. (C) The total distance traveled in the novel arm of the Y maze. (D) The frequency of entries into the novel arm of the Y maze. (E-G) The open field test for WT mice, APP/PS1 mice, and APP/PS1 mice treated with PPD or OA. (E) Representative occupancy plots showing the areas in which the mice spent the most time during the open field test. (F) The mean distance traveled within the center of the arena during the open field test. (G) The mean time spent within the center of the arena during the open field test. n = 5–6 mice per group. Error bars represent the mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, compared with the WT group; #p < 0.05, compared with the APP/PS1 group. PPD, 20(S)-protopanaxadiol; OA, oleanolic acid; WT, wild type; SD, standard deviation.