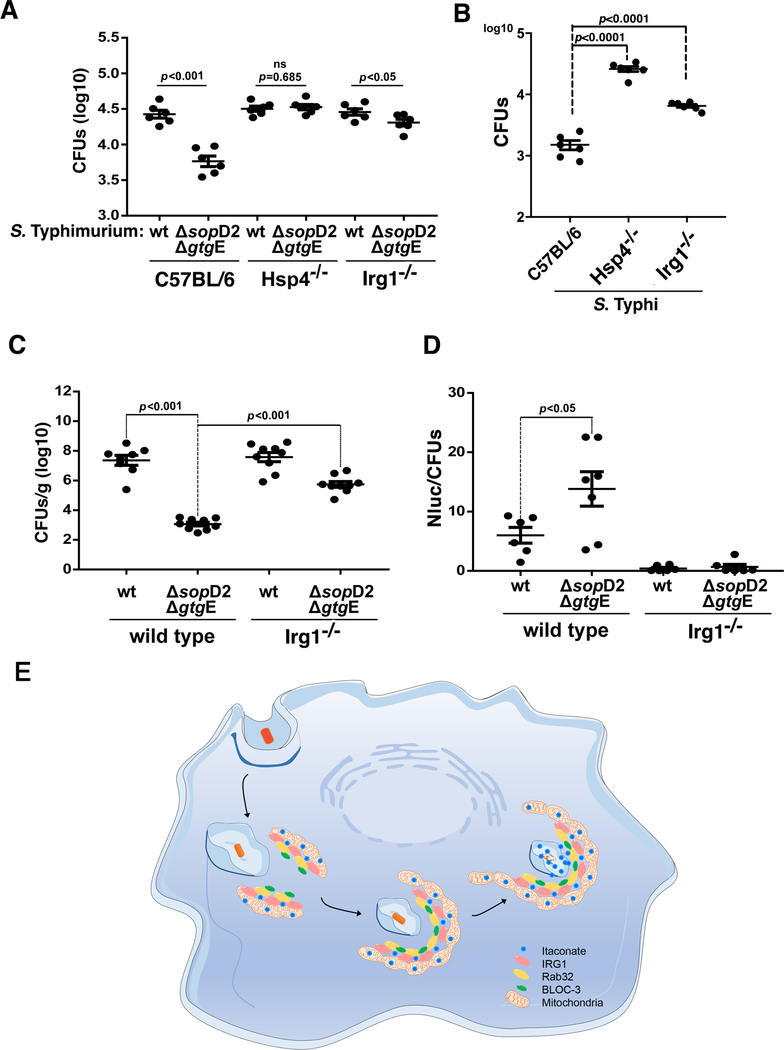
Fig. 4. Susceptibility of IRG1-deficient mice to Salmonella infection.
(A and B) Bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) obtained from C57BL/6 (WT), Hsp4−/−, or IRG1−/− mice were infected with wild-type S. Typhimurium (MOI=5), its ΔgtgE ΔsopD2 mutant derivative (MOI=5) (A), or wild-type S. Typhi (MOI=10) (B), and the number of CFU was determined 9 hours after infection. Each circle represents the CFU in independent measurements; the mean ± SEM of all the measurements and p-values of the indicated comparisons (two-sided Student’s t test) are shown. (C and D) C57BL/6 (wild-type) or IRG1−/− mice were intraperitoneally infected with wild-type or ΔgtgE ΔsopD2 S. Typhimurium (as indicated) (102 CFU). Five days after infection, bacterial loads in the spleen of the infected animals were determined (C). Alternatively, mice were intraperitoneally infected with the same strains (104 CFU) and the levels of luciferase activity in spleen lysates was quantified 24 hours after infection (D). Each circle in (C) represents the bacterial loads of the spleen of an individual animal, and in (D) represents the luciferase levels in the spleen of an individual animal normalized to the CFU. The mean ± SEM of all the determination and p-values of the indicated comparisons (two-sided Student’s t-test) are shown. (E) Model for the mechanism of Rab32—BLOC3-mediated itaconate delivery to the Salmonella-containing vacuole. Upon infection, the mitochondrial network repositions to surround the incoming bacteria, and the resulting close interaction between the mitochondria and the Salmonella-containing vacuole results in the Rab32—BLOC3 dependent delivery of itaconate, which is synthesized in the mitochondria by IRG1.