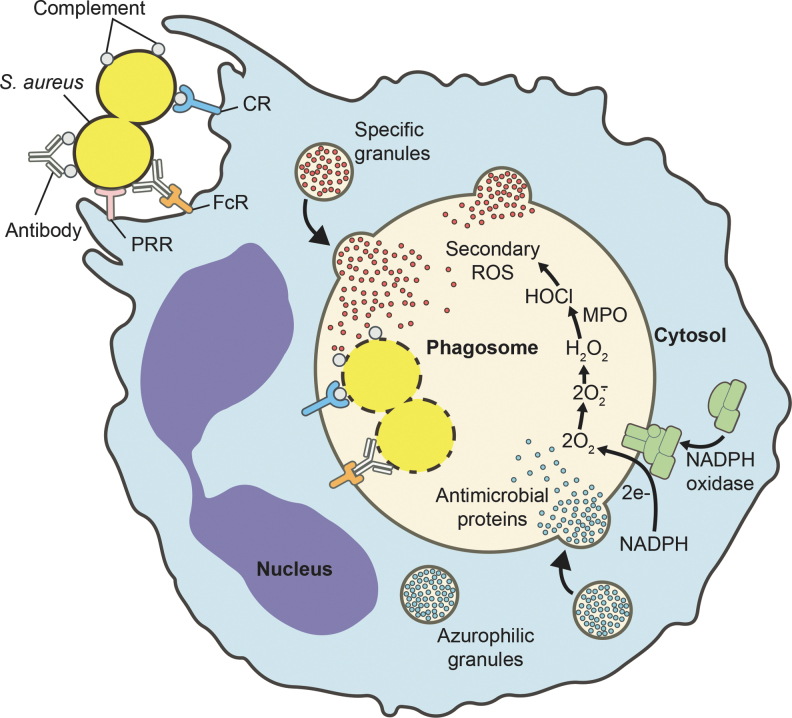
FIG. 5.
Neutrophil phagocytosis and activation. Neutrophil phagocytosis of S. aureus and subsequent intracellular microbicidal processes. Specific and azurophilic granules fuse with the phagosome, thereby enriching the lumen of the vacuole with antimicrobial peptides and proteins. In addition, the NADPH oxidase assembles at the phagosome membrane and produces superoxide, which is converted to other ROS. CR, complement receptor; FcR, antibody Fc receptor; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; ROS, reactive oxygen species.