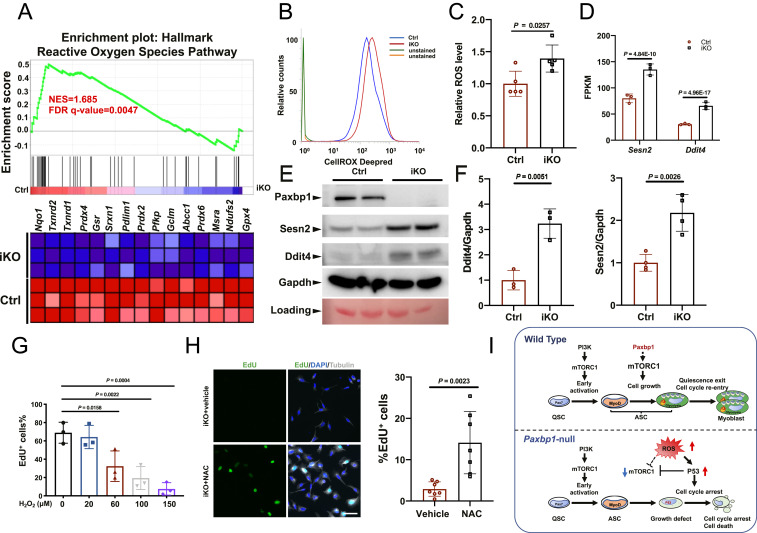
Fig. 6.
Paxbp1-dependent redox regulation influenced the mTORC1 and p53 signaling and cell-cycle reentry of QSCs. (A) GSEA plot showing the defective ROS pathway in Paxbp1-null ASCs. (B) A representative flow cytometry plot showing increased ROS levels in Paxbp1-null ASCs directly isolated from Ctrl and iKO mice at 1 dpi. (C) Quantification of relative ROS levels in B (n = 5 mice per group). (D) Mean FPKM values for Sesn2 and Ddit4 based on our RNA-seq data. (E) A representative Western blot showing the protein levels of Sesn2 and Ddit4 in ASCs after 24 h in culture. (F) Quantification of data in E by densitometry (n ≥ 3). (G) FISCs from wild-type adult mice were cultured for 40 h with EdU in the absence or presence of different doses of H2O2 before fixation followed by staining for EdU. The percentage of EdU+ ASCs over total ASCs is shown (n = 3 independent experiments). (H) FISCs from iKO mice were cultured in the presence of EdU with or without NAC (5 mM) for 60 h before fixation followed by staining for EdU and tubulin. Quantification of the percentage of EdU+ ASCs over total ASCs (n = 7 independent experiments) is also shown. (I) Schematic diagrams summarizing key findings from our work. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (Scale bar, 50 µm.)