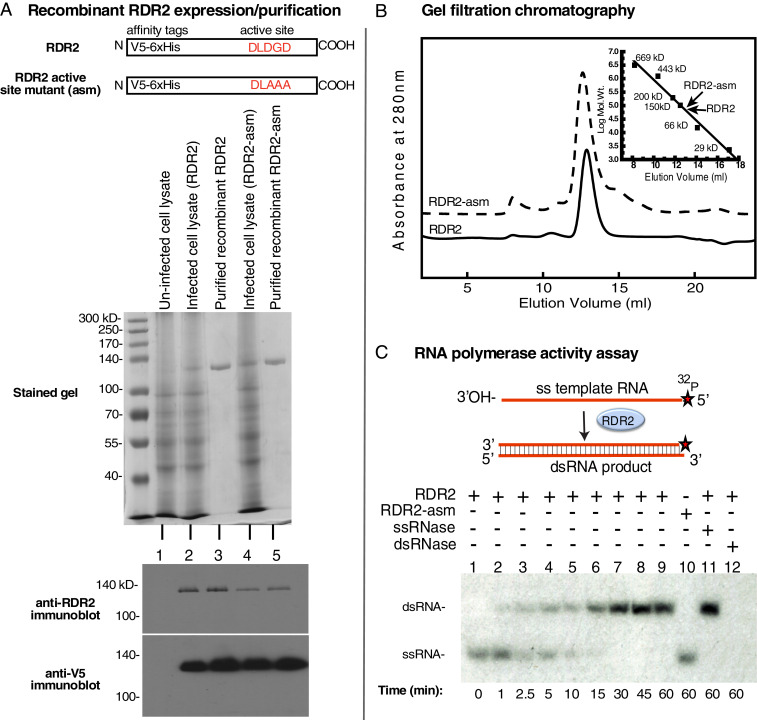
Fig. 1.
Purification and activity of recombinant RDR2. (A) The cartoons depict constructs for WT RDR2 or an active site mutant (asm) that has amino acids of the magnesium binding site changed to alanines. Both proteins have N-terminal V5 epitope tags and 6× His tags. The stained SDS-PAGE gel shows lysates of uninfected High Five insect cells, cells infected with the RDR2 or RDR2-asm baculovirus vectors, and the purified proteins. Anti-RDR2 or anti-V5 immunoblots of the samples are shown at the bottom. (B) Gel filtration chromatography profiles of recombinant RDR2 (solid line) and recombinant RDR2-asm (dashed line). Inset shows a semilog plot comparing elution volumes of protein mass standards, RDR2 and RDR2-asm. (C) Conversion of a 37-nt ssRNA, labeled on its 5′ end with 32P, into dsRNA by recombinant RDR2. Lanes 1–9, time-course of conversion of ssRNA into dsRNA. Lane 10, catalytically dead RDR2-asm was substituted for WT RDR2. Lanes 11 and 12, reaction products treated with a ssRNA-specific RNase, RNase ONE, or dsRNA-specific RNase, RNase V1. Reaction products were resolved on a 15% polyacrylamide native gel and visualized by autoradiography.