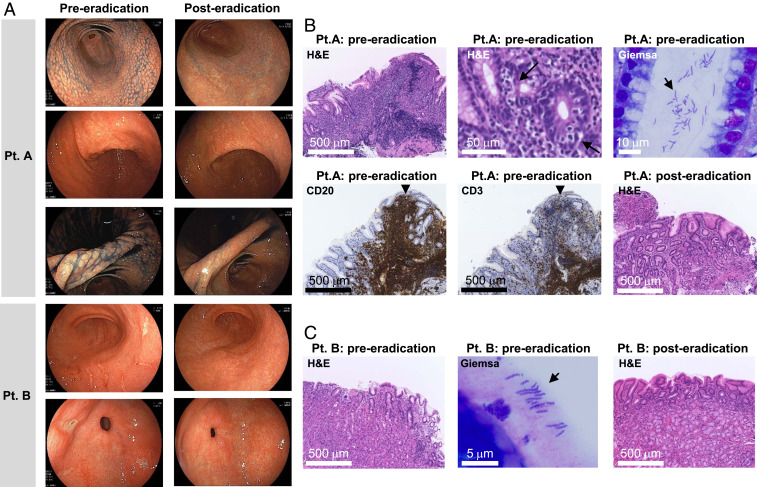
Fig. 2.
Endoscopic and histological images from H. suis–infected patients. (A) Endoscopic images obtained from patient A and patient B pre- and posteradication. Patient A: Nodular gastritis from the antrum to the angle and the mucosal thickening in the angle of the stomach, endoscopically observed preeradication, improved 9 mo after eradication. Patient B: The open and linear multiple gastric ulcers observed before eradication disappeared. Histological examination of gastric biopsies obtained from patient A (B) and patient B (C) pre- and posteradication. Patient A: Preeradication, diffuse infiltration of lymphocytes and lymphoepithelial lesion (arrow) were observed by H&E staining. Immunostaining of infiltrating lymphocytes within the follicle was positive for CD20 and negative for CD3. Improvement of diffuse infiltration of lymphocytes and improvement of lymphoepithelial lesions were confirmed 3 mo after eradication. Patient B: Improvement of an infiltration of neutrophils observed by H&E staining pretreatment was confirmed posteradication. In both patients, bacteria with spiral morphology very different from that of H. pylori were observed by Giemsa staining.